서 언
농업에서 작물보호제는 노동력 절감, 농산물의 안정적인 생산성 확보 및 품질향상 등을 위해 사용되는 농자재이다. 다양한 농자재 중에서 유기 합성 제초제는 2,4-D 개발 이후 본격적으로 사용되었으며, 저렴한 생산비용 및 우수한 제초효과를 발휘하기 때문에 전 세계적으로 유용하게 사용되고 있다. 그러나 1980년대 트리톤계 4-hydroxyphenlypyruvate dioxygenase (HPPD) 저해제(Prisbylla et al., 1993; Schultz et al., 1993; Secor, 1994) 개발 이후 새로운 작용점으로 상업화된 제초제는 없는 실정이다. 제초제 신규 작용점들에 대한 연구는 지속적으로 이루어 지고 있으나 효율성과 경제성을 확보하지 못해 새로운 제초제 개발은 이루어지지 않고 있다(Krachmer et al., 2014). 유기합성 제초제는 매우 유용한 잡초방제 수단이지만 다음과 같은 다양한 문제점들이 대두되어 글로벌 이슈가 되고 있다. 즉, 동일한 계열의 제초제 연용에 따른 저항성 잡초 발생, paraquat에서의 인축독성과 glyphosate의 발암성물질분류 등으로 인한 안정성 문제, 환경과 생태계에 미치는 영향 및 잔류독성 등 심각한 악영향을 미치고 있다(Shim et al., 1992). 이러한 문제점들을 해결하기 위한 방안으로 신규 작용점을 발굴하거나 합성농약을 대체할 수 있는 미생물 또는 식물 등 천연물 소재의 저독성 고기능소재의 바이오 작물보호제 개발이 주목받고 있다. 천연물소재의 바이오 작물보호제로는 미생물의 병원성을 이용한 미생물 농약과 식물 추출물 또는 미생물의 대사체를 사용하는 천연물 농약이 있다. 천연물 기반의 바이오 작물보호제는 기존 합성 농약과는 다른 독특한 작용특성을 발휘할 가능성이 크고, 상대적으로 인축독성 및 환경오염에 대한 안전성을 확보할 가능성이 높다는 장점을 갖는다. 천연물 기반 제초활성 후보소재 발굴은 다양한 원료에서 가능하지만, 최근 들어서는 특히 방선균과 같은 토양 미생물(Duke et al., 1996; Satoh et al., 1993)에서 후보소재 탐색이 활발하게 연구되고 있다.
토양 방선균 대사체를 활용한 제초제로 Streptomyces hygroscopicus가 생산하는 bialaphos (Bayer et al., 2004; Duke et al., 1996)는 상업화된 대표적인 제초제이며, 새로운 제초제 개발 연구를 위한 미생물 기반의 생리활성물질 발굴 연구도 활발히 이루어 지고 있다(Tachibana and Kaneko, 1986). 특히 방선균은 지금까지 개발된 항생물질의 70%를 차지하고 있으며, 제초활성물질로는 Streptomyces saganonensis로부터 생산된 herbicidin과 herbimycin이 있으며(Chang et al., 2006; Li et al., 2003), Streptomyces viridichromogenes에서 anismycin, Streptomyces albus subsp. chlorinus NRRL B-24108에서 albucidin (Hahn et al., 2009), glufosinate-ammonium은 Streptomyces viridichromogenes와 Streptomyces hygroscopicus에서 분리되었다(Hoerlein, 1994). 방선균이 생산하는 이차대사산물을 이용하여 제초제로 사용할 경우 유기합성제초제보다 상대적으로 독성이 적고, 토양에서 생분해가 빨라(Hoagland, 1990) 자연친화적이며, 대사체의 화학구조를 활용하여 친환경적인 신물질의 제초제 합성을 할 수 있는 장점을 가진 소재로 주목받고 있다(Joseph et al., 2012; Saxena and Pandey, 2001). 본 연구팀에서는 바이오 제초활성 소재 발굴을 위한 방안으로 전국의 국·공립공원, 수목원, 섬지역 및 해안가, 비농경지 등의 토양으로부터 방선균만을 분리 배양하여 토양 방선균 라이브러리를 구축해서 제초활성 후보소재를 탐색하는 연구를 지속적으로 수행하고 있으며, 그 중 제초활성이 우수하고 독특한 살초증상을 발현하는 Streptomyces achromogenes KR-1901이라는 균주를 선발하였다.
따라서 본 연구에서는 선발 방선균 Streptomyces achromogenes KR-1901 균주의 분리 및 동정, 농경지 문제잡초와 생태계교란 식물에 대한 방제효과, 작물 선택성, 기존 제초제와의 특성 비교 등을 통해 바이오 제초제로서의 활용 가능성을 확인해 보고자 수행하였다.
재료 및 방법
방선균 분리 및 배양
시료는 대청호 부근 산림지역에서 지표면 10-15 cm 깊이의 토양을 채취하여 저온고에 보관하며 사용하였다. 토양 도말을 위해 토양 시료는 풍건 후 멸균증류수로 희석하여 토양 현탁액을 만든 뒤 HV한천(Humic acid-Vitamin agar)배지(0.1% humic acid: Dissolved in 0.2 N NaOH, 0.05% Na2HPO4, 0.171% KCl, 0.005% MgSO4, 0.001% FeSO4·7H2O, 0.002% CaCO3, vitamin B complex trace, 50 ppm cycloheximide, pH 7.0) (Hayakawa et al., 1987)에 도말하여 방선균으로 보이는 균총들을 Bennett’s agar (BA; 1% glucose, 0.1% yeast extract, 0.2% Bacto-peptone, 0.1% beef extract, 1.5% agar/1 L dry weight [D.W]) (Hesseltine et al., 1954) plate에 계대배양하여 방선균만을 선택적으로 순수 분리하였다. 순수 분리된 방선균의 활성평가를 위한 배양은 GSS 액체배지(1% soluble starch, 2% glucose, 2.5% soybean meal, 0.1% beef extract, 0.4% yeast extract, 0.2% NaCl, 0.025% K2HPO4, 0.2% CaCO3/1 L D.W)에 접종하여 27℃, 150 rpm으로 8일간 진탕배양한 후 배양액을 원심분리(8,000 rpm, 15 min)하여 균체를 제거한 배양여액으로 활성평가를 위한 검정시료로 사용하였다(Kim et al., 1989).
후보균주 선발 스크리닝
구축된 방선균 라이브러리로부터 제초활성 후보균주 선발을 위한 스크리닝은 바랭이를 이용하여 수행하였다. 바랭이 종자는 한국화학연구원 포장에서 채종하여 4-6℃의 저온고에 보관하며 사용하였다. 표면적 38.5 cm2 polystyrene cup에 원예용상토를 충진하고 20-25립의 종자를 파종하여 온실조건(30±5℃, 광/암=14/10 h)에서 관리하였다. 2-2.5엽기가 되었을 때 각 배양여액 5 mL에 Tween-20이 0.1%가 되도록 첨가하여 바랭이에 분무경엽처리하였으며, 처리 5일 및 10일 후에 달관조사(0: 효과 없음, 100: 완전고사)하였다.
균주 분류 및 동정
공시 균주는 16s rRNA의 염기서열을 분석하여 GenBank database의 염기서열과 비교하고 유사도가 높은 후보군 20종을 Clustal W를 이용하여 정렬하여 Neighbour-Joining Method (PHYDIT program version 3.0)을 통해 Polygenetic tree를 작성하여 동정하였다.
선발균주의 바랭이 생육시기별 제초활성 평가
저온상태로 보관중인 바랭이 종자를 표면적 38.5 cm2 polystyrene cup에 원예용상토(Punong Company, Gyeongju, Korea)을 충진하고 20-25립씩 파종하여 온실조건(30±5℃, 광/암=14/10 h)에서 관리하여 바랭이의 생육이 1.5, 2.5, 4엽기가 되었을 때 선발된 균주 배양여액을 x1, x1/2, x1/4 및 x1/8 농도로 희석조제(Tween-20, 0.1% 포함)하여 포트당 5 mL를 경엽처리하였으며, 처리 7일 후 달관조사(0; 효과없음, 100; 완전고사)하였다.
토양 및 경엽처리 제초활성 평가
표면적 350 cm2의 사각플라스틱 포트에 화본과잡초 5종과 광엽잡초 5종을 파종하여 온실조건(30±5℃, 광/암=14/10 h)에서 관리하였다. 토양처리는 사양토를 충진하여 파종 1일 후에 배양여액의 처리농도가 x1, x1/2, x1/4 및 x1/8이 되도록 희석조제(Tween-20, 0.1% 포함)하여 포트당 14 mL를 처리하고 처리 10일 및 20일 후에 외형적인 증상과 살초정도를 달관조사(0; 효과 없음, 100; 완전방제)하였다. 경엽처리는 원예용상토와 수도용상토를 5:2 (v/v)로 조제하여 충진하고 파종 12일 후에 토양처리와 동일하게 처리하였으며, 7일 후에 달관조사하였다.
작물선택성 평가
선발 균주 배양여액으로 작물에 대한 약해를 평가하기 위하여 표면적 20 cm2 polystyrene cup에 원예용상토를 충진 한 후, 벼, 밀, 보리 종자는 8립씩 파종하였고, 토마토 및 고추 종자는 육묘상에 파종하였다가 본엽이 완전히 전개된 후에 각각 1개체씩을 동일한 cup에 이식하여 온실조건에서 관리하였다. 파종 후 벼와 고추는 27일, 토마토는 20일, 밀과 보리는 7일째 KR-1901 배양여액을 x1, x1/2, x1/4 및 x1/8 농도로 희석조제(Tween-20, 0.1% 포함)하여 컵당 5 mL로 분무경엽처리하였다. 처리 7일 후에 약해 정도를 달관조사(0; 효과 없음, 100; 완전고사) 하였다.
살초스펙트럼 평가
선발 균주의 살초스펙트럼을 확인하기위해 경엽처리에서 사용한 잡초 이외에 20초종의 잡초를 대상으로 수행하였다. 원예용상토와 수도용상토를 5:2 (v/v) 비율로 조제하여 표면적 350 cm2 사각플라스틱 포트(가로22 cm × 세로16 cm)에 20종의 종자를 2 (A, B)개 포트로 나누어 파종하였다. A포트에는 존슨그래스를 포함한 화본과 4종, 사초과인 금방동사니 1종과 털비름을 포함한 광엽 5종을 파종하고, B포트에는 블랙그래스를 포함한 화본과 5종과 쇠비름을 포함한 광엽 5종을 파종하였다. 파종 후 동일한 온실조건에서 관리하다가 파종 후 12일 후에 선발 균주 배양여액을 x1, x1/2 및 x1/4 농도로 희석조제하여 분무경엽처리하고 7일 및 14일 후에 달관조사(0; 효과 없음, 100; 완전고사)하였다.
생태계교란식물 가시박에 대한 살초활성
저온 상태로 보관중인 가시박 종자를 표면적 350 cm2 사각플라스틱 포트에 원예용상토를 충진하여 파종하고 동일한 온실조건(30±5℃, 광/암=14/10 h)에서 관리하였다. 떡잎이 지상부로 출현했을 때 표면적 38.5 cm2 polystyrene cup에 이식하여 3-4엽기가 되었을 때 균일한 개체를 선정하여 사용하였다. 처리농도는 배양여액을 x1, x1/2, x1/4 및 x1/8 농도로 희석조제(Tween-20, 0.1% 포함)하여 컵당 5 mL로 분무경엽처리하였다. 한편 포장시험은 충청남도 부여군 소재의 가시박이 우점하고 있는 야산 지역에 1 m2로 처리구를 조성하여 온실시험과 동일한 농도의 배양여액을 200 L·10 a-1 양으로 경엽처리하였다.
기존 제초제와의 활성비교
상용화되어 있는 제초제와의 살초력 정도 및 약효발현 속도 등을 비교해 봄으로서 선발균주의 살초특성을 확인해 보고자 실험하였으며, 선발 제초제로는 비선택성제초제 paraquat, glyphosate, glufosinate-ammonium, bialaphos를 대상으로 수행하였다. 대상잡초는 표면적 350 cm2의 사각플라스틱 포트에 원예용상토를 충진하고 미국개기장을 포함한 화본과 5종과 까마중을 포함한 광엽 5종을 파종하여 온실조건(30±5℃, 광/암=14/10 h)에서 관리하였다. 처리 농도는 기존제초제의 경우 2, 0.5 및 0.125 kg·a.i·ha-1, 선발 균주는 배양여액의 x1, x1/2, x1/4 희석액(Tween-20, 0.1% 포함) 이었다. 각 처리는 포트당 14 mL를 경엽처리하였으며, 처리 7일 후에 달관조사(0; 효과 없음, 100; 완전고사) 하였다.
결과 및 고찰
후보균주 선발
대청호 부근 산림지역으로부터 토양시료를 채취하고 방선균을 순수 분리하여 토양 방선균 라이브러리를 구축하였으며, 바랭이를 대상으로 방선균 배양여액(x1)의 제초활성을 평가하였다. 제초활성을 평가한 방선균 중 살초력이 우수한 후보방선균을 1차로 선발하였다. 1차 선발된 방선균 중 배양여액을 x1, x1/2, x1/4의 농도로 희석하여 처리했을 때 살초력이 우수하면서 농도의존적인 반응을 보이는 방선균을 후보균주로 선발하여(Fig. 1) Streptomyces sp. KR-1901로 명명하였다.

Fig. 1. Dose response of Streptomyces sp. KR-1901 broth filtrate to Digitaria sanguinalis in a greenhouse condition. Herbicidal activity was determined by visual injury (0: No injury, 100: Complete death) at 5 days after treatment. The representative pictures were taken 5 days after foliar application. CK: Check; DAT: Days after treatment.
공시균주 분류 및 동정
선발 균주를 ㈜마크로젠에 의뢰하여 16s rRNA 유전자 염기서열 분석을 통하여 동정하였으며, 유전자 상동성 검색에서 Streptomyces achromogenes NBRC 14001과 99% 이상의 상동성을 나타내어 Streptomyces achromogenes 로 동정되었다(Fig. 2). 동정된 균주를 전자현미경으로 관찰하였을 때 라운드형의 포자가 약 17-20개씩 연결된 형태적 특성을 확인하였다.

Fig. 2. Morphological characteristics of KR-1901 by electron microscope and selection strain KR-1901 identified by 16S rRNA gene homology search. Neighbour-joining tree of KR-1901, Phylogenetic analysis was accomplished by MEGA6 program based on 16S rRNA sequences of KR-1901 and 10species of related Streptomyces.
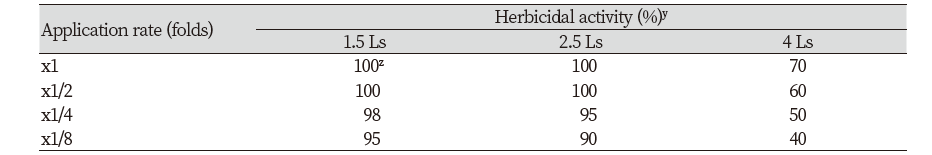
바랭이 생육 시기별 방제효과
선발 균주 배양여액의 바랭이 엽기별 방제효과를 평가했을 때, 1.5 엽기에서 x1, x1/2, x1/4 및 x1/8 처리농도에서의 방제효과는 각각 100, 100, 98 및 95% 이었고, 2.5 엽기의 방제력은 각각 100, 100, 95 및 90% 이었으며, 4 엽기에서의 방제효과는 각각 70, 60, 50 및 40%이었다(Table 1; Fig. 3). 선발 균주 배양여액을 바랭이에 처리하면 24시간 이내에 외형적으로 증상이 발현되어 매우 속효성이었으며, 발현되는 살초증상으로는 잎 전체가 고사(leaf burn down)되거나 잎 중간이 꺾이면서 괴사(necrosis) 증상도 관찰되었다.
잡초방제를 위한 제초제 사용에서 가장 중요한 것은 대상 잡초에 따라 적절한 방제시기에 처리를 하는 것이 가장 효율적인 방제 방법이 될 것이다. 선발 균주 배양여액의 바랭이에 대한 방제효과는 1.5 엽기 및 2.5 엽기에서는 x1/8 처리농도까지 90% 이상이었지만, 4엽기에서는 배양 원액에서도 완전한 방제가 이루어지지 않았다. 따라서 바랭이를 대상으로 하는 선발 균주의 잡초방제는 2.5엽기 이하의 생육시기에 처리를 하는 것이 효율적인 방법으로 판단되었다.
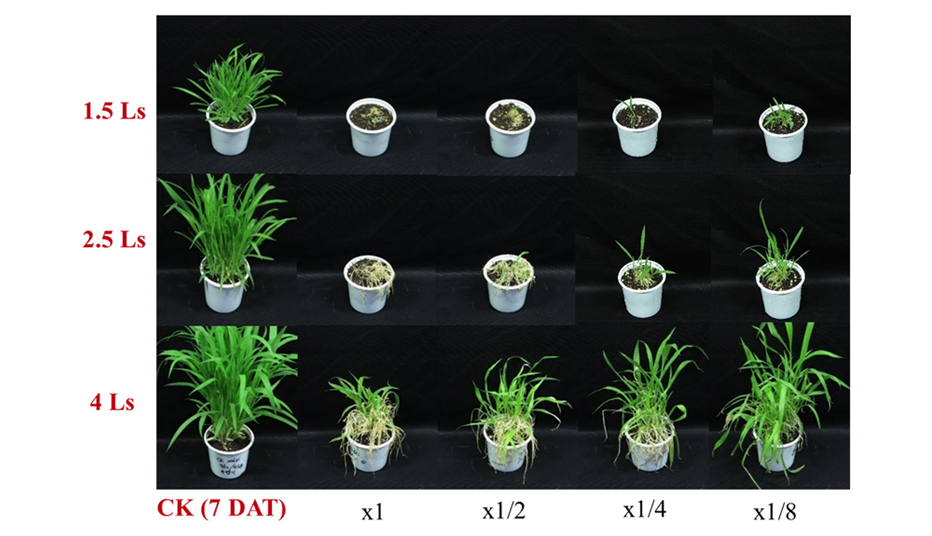

Fig. 3. Herbicidal activity of foliar application of Streptomyces achromogenes KR-1901 broth filtrate to Digitaria sanguinalis with leaf stage in a greenhouse condition. Herbicidal activity was determined by visual injury (0: No injury, 100: Complete death) at 7 days after treatment. The representative pictures were taken 7 days after foliar application. Ls: Leaf stage; CK: Check; DAT: Days after treatment.
토양처리 및 경엽처리 방제효과
선발 후보소재의 토양처리제로서의 가능성은 잡초 종자의 발아 또는 출현의 억제, 출현 후 생육억제 또는 황화, 백화, 괴사와 같이 외형적으로 발현되는 살초증상을 통해서 확인할 수 있을 것이다. 선발 소재 KR-1901 토양처리 결과, 처리 10일 후에 모든 초종에서 발아저해는 없었으나 무처리구와 비교했을 때 생육억제가 관찰되었고, 20일 후에는 생육억제 현상이 더욱 뚜렷이 나타나는 것을 확인하였다(Fig. 4). 다만 생육억제 이외의 외형적으로 발현되는 다른 증상은 관찰되지 않았다.
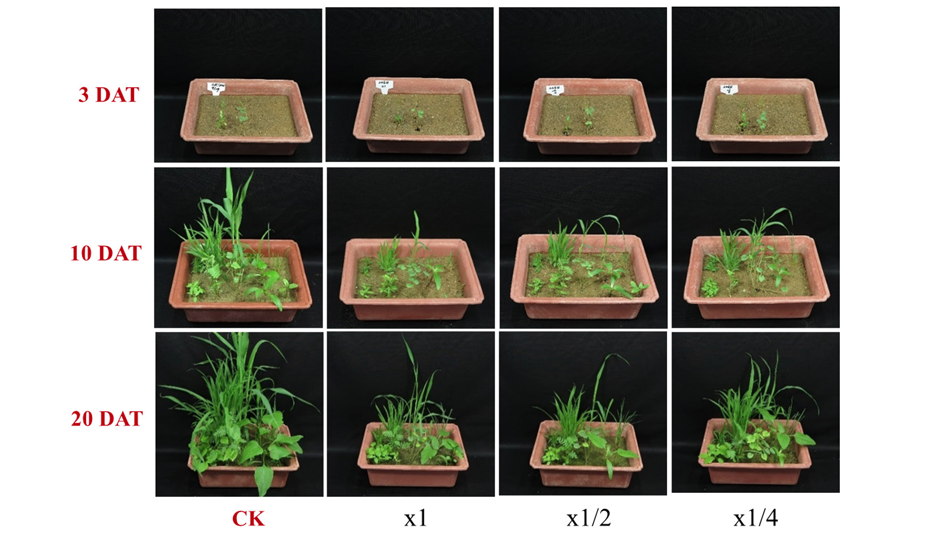

Fig. 4. Herbicidal activity of soil treatment of Streptomyces achromogenes KR-1901 broth filtrate to several weed species in a greenhouse condition. The representative pictures were taken 10 and 20 days after foliar application. Grass weeds: Panicum dichotomiflorum Michx, Digitaria sanguinalis, Sorghum bicolor, Echinochloa cruss-galli, Agropyron tsukusinense. Broadeleaf weeds: Solanum nigrum, Aeschynomene indica, Abutilon avicennae, Xanthium strumarium, Calystegia sepium var. japonicum. CK: Check; DAT: Days after treatment.
농작물 재배지에서 통상 잡초의 성장은 작물보다 빠르게 진행되어 작물보다 먼저 우점하여 작물과 경합하여 생육에 피해를 야기한다(Kim et al., 2017). 선발 소재 KR-1901의 토양처리는 다양한 잡초에서 뚜렷한 생육억제 효과가 있기 때문에 목적으로 하는 작물재배 이전에 토양에 처리하면 초기에 발생하는 잡초의 생육을 억제시킴으로서 작물재배 후 잡초와의 경합에서 우위를 점하게 되어 정상적인 작물생장이 가능하게 될 것으로 판단된다.
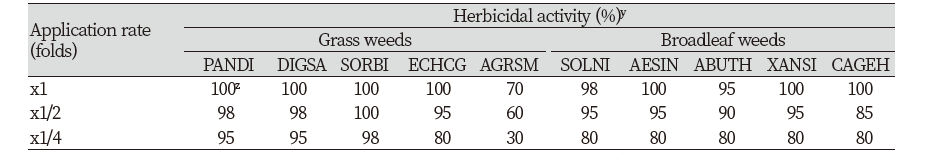
KR-1901의 배양여액을 화본과잡초 5종과 광엽잡초 5종에 경엽처리하였을 때 원액의 경우 개밀을 제외한 4종의 화본과잡초에서 100%의 방제효과를 보였고, 5종의 광엽잡초에서는 95% 이상의 아주 우수한 방제효과를 나타내었다. 또한, x1/4 처리농도에서도 개밀을 제외한 9개 초종에서 80% 이상의 방제효과를 보였다(Table 2; Fig. 5). 경엽처리 시 발현되는 살초증상은 광엽잡초에서는 처리 초기에는 수침상 반점(water soaked)으로 시작하여 고사(desiccation)로 진행되었고, 화본과잡초의 경우 고사 및 잎 중간이 잘록하게 꺾이기도 하고 괴사(necrosis) 증상이 발현되기도 하였다. 또한, 화본과잡초와 광엽잡초 간 제초활성 차이는 없었다.

Fig. 5. Herbicidal activity of foliar application of Streptomyces achromogenes KR-1901 broth filtrate to several weed species in a greenhouse condition. Herbicidal activity was determined by visual injury (0: No injury, 100: Complete death) at 7 days after treatment. The representative pictures were taken 7 days after foliar application. Grass weeds: Panicum dichotomiflorum Michx, Digitaria sanguinalis, Sorghum bicolor, Echinochloa cruss-galli, Agropyron tsukusinense, Broadeleaf weeds: Solanum nigrum, Aeschynomene indica, Abutilon avicennae, Xanthium strumarium, Calystegia sepium var. japonicum. CK: Check; DAT: Days after treatment.
일반적으로 천연제초활성 물질들은 주로 접촉형, 비선택성 살초효과를 나타내는데, 잎이나 줄기에 화염상반점(burn-down) 증상을 보이다가 약효 지속기간이 짧아 일정시간이 경과하면 재생되는 특징을 갖는다(Chun et al., 2002). 선발 소재 KR-1901은 경엽처리했을 때 속효성과 접촉형의 특성을 보이면서 leaf burn-down의 증상을 나타내지만, 처리 후 일정시간이 경과하여도 재생되는 개체가 확인되지 않아 약효 지속력도 높은 것으로 판단되었다.
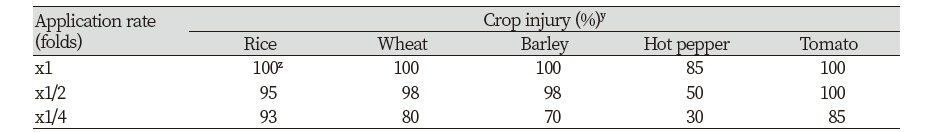
작물선택성
작물에 대한 약해 평가를 위해 벼, 보리, 밀, 고추, 토마토를 대상으로 하여 KR-1901 배양여액을 처리하였다. 배양원액에서는 각각 100, 100, 100, 85, 100% 의 약해를 보였고, x1/2 희석액에서는 95, 98, 98, 50, 100% 로 나타났으며, x1/4 희석액에서도 93, 80, 70, 30, 85% 로 모든 작물에서 재생이 불가능 할 만큼 약해가 발생 되었다(Table 3). 작물 종에 따른 약해는 작물의 종류 및 종자 크기에 따라 차이가 있으며(Ibrahim et al., 2004; Lee et al., 2007), 이러한 원인은 식물에서 제초활성물질의 작용기전이 작물 종에 따라 다를 수 있기 때문이다(Vaughn et al., 1993). 작물에 대한 약해 평가로부터 선발 균주는 국내에서 재배되는 주요 작물에 대한 선택성이 없으므로 비농경지, 과수원, 시설재배지 주변, 논뚝이나 밭뚝 등에서 비선택성 경엽처리제로서의(Choi et al., 2012) 활용방안을 고려할 수 있을 것으로 판단하였다.
살초스펙트럼
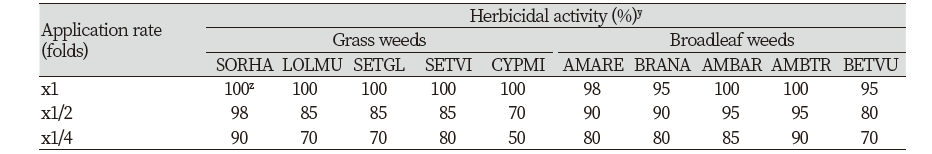
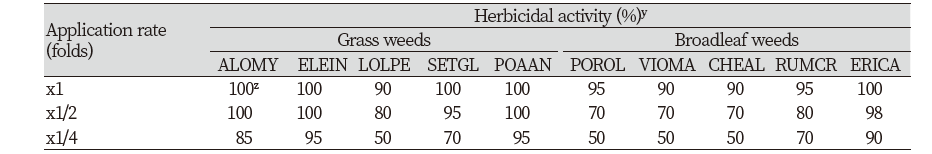
A pot의 화본과 4종 및 사초과 1종과 광엽 5종에 경엽처리한 결과, 배양 원액에서 존슨그래스, 이탈리안 라이그래스, 금강아지풀, 강아지플 4종의 화본과잡초와 사초과인 금방동사니는 완전방제되었고, 5종의 광엽잡초 모두 95% 이상의 높은 방제효과를 보였다(Table 4; Fig. 6A). B pot의 화본과잡초 5종과 광엽잡초 5종에 경엽 처리하였을 때, 배양원액에서 블랙그래스, 왕바랭이, 금강아지풀, 새포아풀 등 4종의 화본과잡초 및 광엽잡초 망초에서 완전방제되었고, 다른 초종에서도 90% 이상의 높은 방제효과를 나타내었다(Table 5; Fig. 6B). 배양여액 x1/2 처리농도에서도 모든 잡초에서 70% 이상의 양호한 방제효과를 나타냈는데, 특히 왕바랭이, 새포아풀, 망초의 경우에는 x1/4 처리농도에서도 90% 이상의 높은 방제효과를 보였다.
이상의 결과와 같이 선발 방선균 KR-1901 균주 배양여액은 잡초 종류에 관계없이 다양한 초종에서 우수한 방제효과를 보이고 있어 살초스펙트럼이 매우 넓은 비선택성 제초제로서 유용하게 활용이 가능할 것으로 판단하였다.
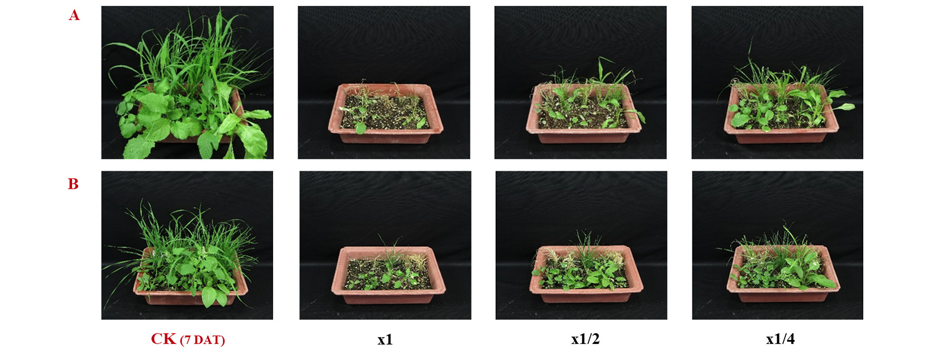
Fig. 6. Herbicidal spectrum of Streptomyces achromogenes KR-1901 broth filtrate to several weed species (A and B pot) in a greenhouse condition. The representative pictures were taken 7 days after treatment. A pot - Grass weeds; Sorghum halepense, Lolium multiflorum, Setaria glauca, Setaria viridis. Cyperaceae: Cyperus microiria. Broadeleaf weeds: Amaranthus retroflexus, Brassica napus, Ambrosia artemisiifolia, Ambrosia trifida, Beta vulgaris var. B pot - Grass weeds: Alopecurus myoosuroides, Eleusine indica, Lolium perenne, Setaria glauca, Poa annua. Broadeleaf weeds: Portulaca oleracea, Viola mandshurica, Chenopodium album, Rumex crispus, Erigeron canadensis. CK: Check; DAT: Days after treatment.
생태계교란식물 가시박에 대한 살초활성
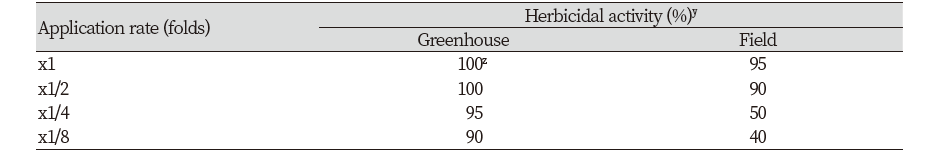
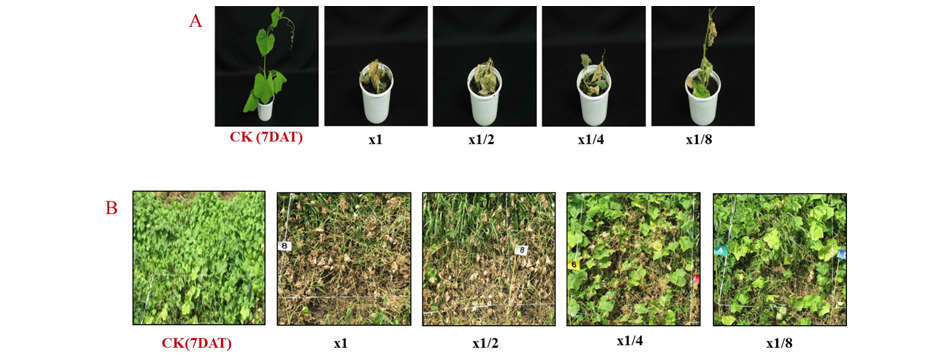
가시박은 환경부에서 지정한 생태계교란식물로서 주요 분포지역이 4대강이나 주요 하천을 포함한 수변과 우리 생활주변이기 때문에 유기합성 제초제의 사용이 제한적일 수 밖에 없다(Copping and Duke, 2007). 또한, 물리적 방제는 많은 노동력이 필요하고 예취로는 번식속도가 제거속도보다 빨라 확산을 막기가 어려워 환경친화적이면서 효율적인 제거기술개발이 필요하다(Kim et al., 2018). 온실조건에서 가시박에 선발균주의 배양여액을 처리하면 x1, x1/2, x1/4 및 x1/8 농도에서 처리 7일 후 각각 100, 100, 95 및 90% 방제 되었고, x1/8 희석액에서도 처리 4일 이후에 생장점이 고사되기 시작하여 10일 후에는 완전히 고사 되었다(Table 6; Fig. 7A). 외형적인 증상은 처리 초기에는 수침상 반점이 형성되기 시작하여 황화(chlorosis)로 진행되었다가 결국 고사로 이어져 사멸되었으며, 처리 후 시간이 경과하여도 재생되는 개체는 확인되지 않았다. 포장시험 결과 처리 1일이 지나면서 외형적인 증상이 발현되기 시작하여 처리 7일 후에는 1/2 희석액까지 90%로 방제효과가 우수하였다(Table 6; Fig. 7B). 주요 증상은 고사(leaf burn-down)였으며, 처리 2주 후에도 재생되지 않아 약효지속력이 우수함을 확인하였다. 그러나 x1/4 과 x1/8 희석액에서의 방제효과는 각각 50 및 40%로 약한 것으로 나타났다.
이상과 같이 온실 및 포장실험을 통하여 선발 균주 배양여액은 생태계교란식물 가시박에 대해 천연물 잡초 방제제로서의 가능성을 확인할 수 있었다. 그러나 포장조건에서 x1/4 이하 농도에서는 방제효과가 낮기 때문에 균주 개량을 통한 유효제초활성물질 증진, 약효증진 제형 개발, 2-3회 체계처리를 통한 처리방법 개선 등의 후속연구를 통해 해결할 수 있는 방안을 모색할 필요가 있을 것으로 사료된다.
기존제초제와의 살초특성 비교
기존 상용제초제와 KR-1901 배양여액의 살초특성을 비교하였다(Fig. 8). 상용 제초제 중 paraquat는 광합성 전자전달 과정 중 광계 I에서 전자흐름을 차단하여 궁극적으로는 활성산소에 의해 식물체가 고사되는 작용기전을 가진 제초제로(Duke, 1990), 처리 이후 약효발현속도가 가장 빠른 제초제로 알려져 있다(Kirkwood, 2013; William, 1994). bialaphos와 glufosinate-ammonium은 Streptomyces hygroscopicus가 분비하는 2차 대사산물을 이용한 제초제이며(Berdy, 2005), glutamine synthetase를 억제하여 식물체 내에 암모니아가 생성되고 이는 광합성 및 광호흡을 억제하여 단백성분을 고갈시켜 식물체의 고사를 유발하는 제초제이다(Wendler and Wild, 1990). Glyphosate는 식물의 shikimate 경로에서 5-enolpyruvyl-shikimate-3-phosphate (EPSP) 억제하고, 침투성으로 인해 잡초 지상부에 살포되면 뿌리까지 침투하여 식물체가 고사하는 제초제이다.
선발 균주 KR-1901 배양여액의 약효발현 속도는 paraquat보다 느리고, bialaphos와 비슷하였고 glyphosate와 glufosinate-ammonium보다는 빠른 것으로 나타났다. 살초발현 속도는 기존 제초제는 2 kg·a.i·ha-1, 선발균주는 x1 농도에서 처리 3일 후에 paraquat (100%), bialaphos와 KR-1901 (95% 이상), glufosinate-ammonium (40%), glyphosate (30%) 순으로 나타났다. 그러다가 약제처리 7일 이후에는 모든 처리구에서 98% 이상의 방제효과를 나타내었다.
이상의 결과에서 선발 방선균 KR-1901의 살초력은 원액 기준으로 기존 제초제와 대등한 수준이었고, 약효발현속도는 paraquat에 비해서는 약간 늦지만 glyphosate와 glufosinate-ammonium보다는 빠른 살초특성을 보이고 있었다. 향후 기존 상용 제초제와는 차별성을 가지면서 독창적인 살초특성을 발휘할 수 있는 천연물 기반의 친환경적인 제초제로서의 가능성을 확보할 수 있는 추가 연구를 수행하고자 한다.
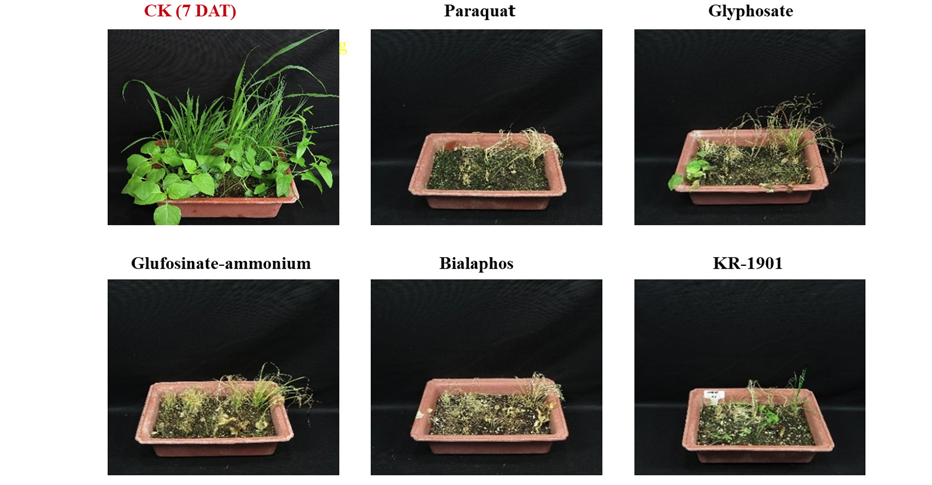

Fig. 8. Herbicidal activity comparison of Streptomyces achromogenes KR-1901 broth filtrate to several commercial herbicides in a greenhouse condition. Commercial herbicides were treated with 2 kg·a.i·ha-1 and KR-1901 was treated with broth filtrate. Grass weeds: anicum dichotomiflorum Michx, Digitaria sanguinalis, Sorghum bicolor, Echinochloa cruss-galli, Agropyron tsukusinense, Broadeleaf weeds: Solanum nigrum, Aeschynomene indica, Abutilon avicennae, Xanthium strumarium, Calystegia sepium var. japonicum. CK: Check; DAT: Days after treatment.
Acknowledgment
This work was carried out with the support of “Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development (Project No. PJ013479)” Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Authors Information
Hwasook Kwak, National Institute of Agricultural Sciences, RDA, Postdoctoral researcher
Youngsook Kim, Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology, Researcher
Jaedeok Kim, Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology, Postdoctoral researcher
Hyejin Kim, Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology, Researcher
Kyoungsoo Jang, Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology, Researcher
Jinwoo Park, National Institute of Agricultural Sciences, RDA, Researcher
Jungsup Choi, Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology, Researcher