서 론
농작물 생산성 향상을 위한 다양한 잡초방제 방법 중에서 상대적으로 저렴한 생산비용과 우수한 방제효과 때문에 전 세계적으로 유기합성 제초제가 유용하게 사용되고 있는데, benzobicyclon
과 mesotrione, tefuryltrione 등과 같은 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPPD) 저해제(Prisbylla et al., 1993; Schultz et al., 1993; Secor et al., 1994)가 개발된 이후 새로운 작용점을 갖는 제초제의 개발 성과가 없는 실정이다. 이와 같은 상황에서 기존의 모방적 기술을 탈피하여 새로운 개념의 제초제 개발이 요구되고 있으며(Choi et al., 2011), 식물이나(Copping and Duke, 2007; Goncalves et al., 2009) 미생물(Bender et al., 1999; Misra, 2005) 등 천연물 기반의 제초활성 후보소재 탐색이 시도되고 있으나 국내의 경우 지금까지는 뚜렷한 개발 성과가 보고된 바는 없다.
천연물 기반의 제초활성 후보소재 탐색을 위한 연구 재료로 방선균(Actinomycetes)이 많이 활용되고 있는데, 특히 토양 방선균을 포함한 Streptomyces 속은 다양한 종류의 2차 대사산물을 합성하기 때문에 학문적·산업적 측면에서 많은 연구자들의 관심을 받고 있다(Joseph et al., 2012). 방선균은 새로운 생리활성물질을 생산할 가능성이 있으며, 이러한 가능성을 제초제 후보소재 탐색을 위한 연구에 적용할 경우 기존 제초제와는 다른 작용기작을 갖는 신물질의 발견도 기대할 수 있을 것이다(Saxena and Pandey, 2001). 토양 방선균 기반의 제초제 개발 사례로는 Streptomyces viridochromogenes가 생산하는 2차 대사산물을 기반으로 하는 bialaphos (Bayer et al., 2004; Duke et al., 1996)와 S. viridichromogenes와 S. hygroscopicus에서 분리된 glufosinate-ammonium (Hoerlein, 1994) 등이 있다.
국내에서 토양 방선균을 활용한 제초활성 후보소재 발굴을 위한 연구로는 토양 방선균 유래 herbicidin의 제초활성(Won et al., 2015), S. scopuliridis KR-001 균주 배양액에 의한 잡초 방제효과(Lee et al., 2013)와 Streptomyces 속에서 유래된 물질 methoxyhygromycin (Lee et al., 2003)이 천연 제초활성 후보소재로서의 가능성이 보고되어 있다.
그 동안 한국화학연구원에서는 천연물 기반의 제초활성 후보소재 탐색 및 발굴을 위한 연구를 지속적으로 수행하고 있다. 이와 같은 천연제초제 후보소재 발굴과 관련하여 전국의 국·공립공원, 수목원, 산림지 또는 비농경지 등의 지역에서 토양 시료를 채취하여 토양 방선균 만을 분리·배양하여 방선균 라이브러리를 구축하고 있으며, 이로부터 제초활성 후보소재 탐색을 하고 있다. 본 연구는 구축된 라이브러리로부터 G-0299 균주 배양액을 확보하여 선행연구를 통해 화본과잡초 중에서 유일하게 바랭이에 대해서만 제초활성이 발현되는 현상을 발견한 바, 생리·생화학적인 반응을 통해 방선균 G-0299의 살초특성을 확인함으로써 새로운 작용 메커니즘을 갖는 신규 제초제 후보소재 발굴을 위한 자료로 활용하고자 수행하였다.
재료 및 방법
방선균 분리 및 배양
방선균 G-0299는 충청남도 대천 부근의 산림 토양으로부터 HV한천(humic acid-vitamin agar) 배지 [0.1% humic acid (dissolved in 0.2 N NaOH), 0.05% Na2HPO4, 0.171% KCl, 0.005% MgSO4, 0.001% FeSO4·7H2O, 0.002% CaCO3, vitamin B complex trace, 50 ppm cycloheximide, pH 7.0]를 사용하여 분리하였으며 Bennett’s agar (BA; 1% glucose, 0.1% yeast extract, 0.2% bacto-peptone, 0.1% beef extract, 2% agar, 1 L water) plate에 계대배양하여 순수 분리하였다. 활성배지로 GSS 액체배지(1% soluble starch, 2% glucose, 2.5% soybean meal, 0.1% beef extract, 0.4% yeast extract, 0.2% NaCl, 0.025% K2HPO4, 0.2% CaCO3)를 사용하였으며 27°C, 160 rpm으로 7일간 진탕 배양한 후 배양액을 원심분리(8,000 rpm, 15분)하여 균체를 제거한 배양 여액을 감압농축(EYELA, N-1200A)하여 활성 평가를 위한 검정시료로 사용하였다.
경엽처리 제초활성 평가
경엽처리 살초력 평가는 바랭이를 포함한 화본과잡초 5종 및 까마중을 포함한 광엽잡초 5종 등 10종의 잡초를 대상으로 저온건조 상태로 보관 중인 종자를 파종하여 온실조건에서 10일 동안 생육시킨 식물체를 사용하였다. 배양 여액 농축 시료를 소량의 아세톤으로 용해시킨 후 약제 조제액(50% 아세톤, Tween-20 0.1% 포함)으로 최종 처리농도가 2,000 µg mL-1이 되도록 희석조제하여 경엽처리하였고, 동일한 온실조건에서 관리하다가 처리 10일 후에 외형적인 증상을 기준으로 달관조사(0; 효과 없음, 100; 완전고사)하였다.
바랭이에 대한 살초력 평가
온실조건(30/25±5°C, light/dark=14/10 h)에서 10일 동안 생육시킨 바랭이를 대상으로 2,000 µg mL-1 농도부터 1/2로 희석하여 31.3 µg mL-1 농도까지 7단계 처리하였다. 배양 여액 농축 시료는 약제 조제액(50% 아세톤, Tween-20 0.1% 포함)으로 최종 처리농도가 되도록 희석 조제하여 경엽처리하였고, 동일한 온실조건에서 관리하다가 처리 5일 및 10일 후에 달관조사(0; 효과 없음, 100; 완전고사)하였다.
화본과잡초에 대한 제초활성 평가
표면적 350 cm2 포트에 원예용상토를 충진하여 새포아풀, 카나리그래스, 강아지풀, 금강아지풀, 호밀풀, 왕바랭이, 존슨그래스 및 바랭이 등 8종의 화본과잡초를 파종하여 온실조건에서 관리하였다. 파종 21일 후에 배양 여액 농축 시료 최종처리 농도를 2,000, 1,000, 500 및 250 µg mL-1로 희석조제하여(Tween-20, 0.1%) 포트 당 14 mL 양으로 처리 후 동일한 온실조건에서 관리하였다. 처리 7일 후에 살초력을 육안으로 달관조사하였다.
광조건에 따른 제초활성 반응 평가
표면적 38.5 cm2 polystyrene cup에 파종하여 온실에서 생육시킨 바랭이에 배양 여액 농축 시료를 2,000 µg mL-1 농도로 조제하여 20 ml/6 pots 양으로 처리한 후 0, 1, 2, 3, 4일 동안 암조건(25°C)으로 두었다가 각각을 온실조건으로 전환하여 8일 후에 살초력 정도를 육안으로 관찰하였다.
광조건에 따른 엽록소 함량에 미치는 영향 평가
온실조건에서 생육시킨 바랭이 제 2엽을 절취하여 3 mm2 내외의 엽 절편을 만들어 1%의 sucrose를 포함하는 1 mM MES buffer (pH 6.8) 7 mL가 담긴 Petri-dish에 0.2 g씩 치상 한 후 최종 처리농도를 2,000 µg mL-1가 되도록 배양 여액 농축 시료를 처리하였다. 처리 후 광조건(25°C, 120 µmol m-2 sec-1)과 암조건(25°C, dark alone)으로 구분하여 관리하다가 48시간 후에 Hiscox와 Israelstam의 방법(Hiscox and Israelstam, 1979)을 이용하여 엽록소 함량을 측정하였다. Petri dish에 있는 엽 절편을 배양액과 분리하여 여과지로 흡습시켜 시험관에 넣고 10 mL의 DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide)를 넣은 다음, 암조건으로 실온에 24시간 동안 두었다. 이때 엽절편의 엽록소는 완전히 추출되었으며, 흡광분광분석기(Beckman, UV-52)를 이용하여 645 nm와 663 nm에서 흡광도를 측정하였다.
총 엽록소의 양은 다음의 식으로 계산하였다.
Chlorophyll (mg/L) = (20.2×A645+8.02×A663)×dilution factor
결과 및 고찰
경엽처리 제초활성
분리 방선균 G-0299의 배양 여액 농축 시료 2,000 µg mL-1 처리농도에서 10종의 잡초에 대한 제초활성 여부를 평가했을 때 광엽잡초 5종에 대한 활성은 없었고, 5종의 화본과잡초 중에서도 바랭이에 대해서만 살초력이 발현되는 독특한 특성이 관찰되었다(Table 1, Fig. 1). 배양 여액 농축 시료를 처리했을 때 까마중, 자귀풀, 어저귀, 도꼬마리, 메꽃 등 5종의 광엽잡초 종에 대해서는 아무런 반응이 없었고, 수수, 돌피, 개밀, 미국개기장 등 4종의 화본과잡초 종에 대해서도 제초활성이 발현되지 않았으나 바랭이에 대해서만 100%의 살초력을 나타냈다. 바랭이에 대해서는 처리 24시간 이내에 외형적인 증상이 발현되기 시작하여 매우 속효성이었으며, 주요 살초증상으로는 처리 초기에 수침상이 발현되다가 시간이 경과함에 따라 완전 고사(desiccation or leaf burn-down)되었으며, 완전 고사되지 않은 일부 개체에서는 백화증상(bleaching)이 발현되었다.
Fig. 1.
Herbicidal activity of foliar application of the isolate G-0299 culture filtrate to five broad leaf and five grass weed species in a greenhouse condition. Herbicidal activity was determined by visual injury (0: no injury, 100: complete death) at 10 days after treatment. The isolate G-0299 effectively controlled only D. ciliaris among 10 weed species with foliar application of 2,000 µg mL-1 concentration (red circle). The representative pictures were taken 10 days after foliar application.

바랭이에 대한 농도반응
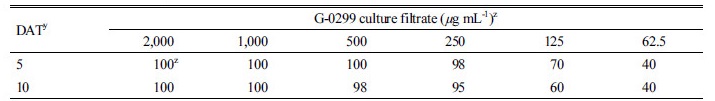
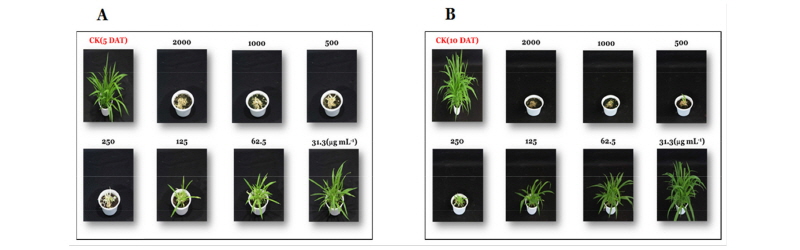
배양 여액 농축 시료 처리 5일 후 2,000, 1,000, 500, 250, 125 및 62.5 µg mL-1 농도에서의 바랭이에 대한 살초력은 각각 100, 100, 100, 98, 70 및 40%로 아주 우수하였다(Table 2). 또한, 10일 후에도 동일한 처리농도에서 각각 100, 100, 98, 95, 60 및 40%로 처리시간이 경과함에도 여전히 우수한 살초력을 유지하고 있었다(Fig. 2A and B). 다만, 125 µg mL-1 처리농도 이하에서는 10일 이후에는 일부 재생되는 개체가 확인되었다. 이와 같이 G-0299는 바랭이에 대해서 농도의존적으로 살초력을 발휘하였으며, 이러한 결과로부터 바랭이에 대해서만 특이적으로 살초력을 발현하는 2차 대사물질을 생산하는 것으로 판단하였다.
Fig. 2.
Herbicidal activity of the isolate G-0299 culture filtrate to D. ciliaris. The culture filtrate showed inhibitory effects on D. ciliaris by foliar application to several concentrations in a greenhouse condition. The representative pictures were taken 5 (A) and 10 (B) days after foliar application.
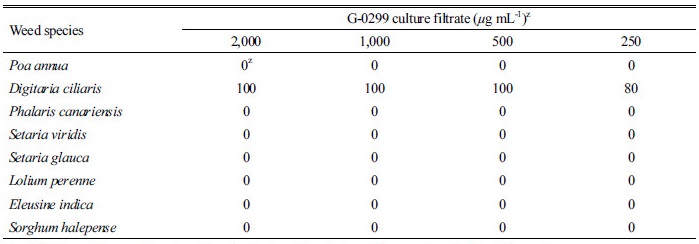
다양한 화본과잡초에 대한 제초활성
방선균 G-0299는 8종의 시험대상 화본과잡초 중에 다른 잡초에 대해서는 반응이 없었고 바랭이에서만 살초효과가 발현되었다. 처리 7일 후 배양 여액 농축 시료 2,000, 1,000 및 500 µg mL-1 처리농도에서의 바랭이에 대한 살초력은 모두 100%였고, 250 µg mL-1 처리농도에서는 80%였다(Table 3). 그러나 바랭이 외 7종의 화본과잡초에서는 제초활성이 없었으며, 처리 4주 후까지도 반응이 없었다. 또한, 화본과잡초 이외 금방동사니와 같은 사초과 잡초에 대해서도 살초력이 발현되지 않았다(자료 미제시). 이와 같은 G-0299의 살초특성은 매우 특이한 현상으로서 기존 개발된 제초제와는 뚜렷한 차별성을 갖는 작용 메커니즘일 것으로 판단되었다.
광조건에 따른 제초활성 반응 평가
선행연구로부터 바랭이에 대한 방선균 G-0299의 살초력은 광조건하에서만 발휘되는 것을 확인한 바 있는데, 광 유·무에 따른 배양 여액 농축 시료의 약효반응 여부를 확인해 보았다. 배양 여액 농축 시료를 바랭이에 처리했을 때, 암조건에서는 아무런 약효가 발현되지 않다가 광조건으로 전환된 이후에 살초력이 발현되는 것으로부터 방선균 G-0299 배양 여액 농축 시료의 살초력 발현은 광의존적인 반응인 것을 확인할 수 있었다(Fig. 3).
배양 여액 농축 시료 처리 후 바로 광조건에 둘 경우에는 서서히 약효가 발현되기 시작하여 처리 일수가 경과함에 따라 지속적으로 살초력이 증가하여 3일 이후에 완전 고사되었다. 그러나 처리 후 1-4일 동안 암조건에 둘 경우에는 반응이 나타나지 않았으며, 광조건으로 전환하면 곧바로 약효가 발현되어 광조사 1일 이후에 완전 고사되었다. 이때 암조건에서 2일 이후에 바랭이 잎의 황변과 괴사가 발현되면서 정상적인 생장이 저해되고 있었는데, 이러한 현상은 무처리의 암조건에서도 동일한 현상이 발현되는 것으로 보아(자료 미제시) 시료에 의한 반응이 아니라 암상태에서 바랭이의 정상적인 생육이 저해되기 때문인 것으로 판단하였다. 이상의 결과는 살초력을 발휘하는 유효성분이 암상태에서 충분하게 식물체 내로 흡수되었다가 광이 조사되면 즉시 약효가 발현되기 때문으로 판단되었다. 이상의 결과로부터 G-0299균 배양 여액 농축 시료는 암조건에서는 약효가 발현되지 않고, 광조건에서만 살초력이 발현되는 전형적인 광의존적 제초활성을 나타내는 것을 확인하였다.
광조건에 따른 엽록소 함량에 미치는 영향
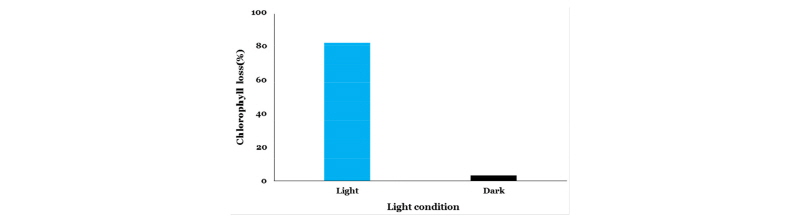
방선균 G-0299 배양 여액 농축 시료 처리 후 광 또는 암조건에서 48시간 경과한 다음 육안으로 관찰했을 때, 암조건에서는 바랭이 엽 절편의 엽색 변화는 없었고(Fig. 4A), 광조건에서는 바랭이 엽색이 변해서 백화되거나 갈변된 모습을 확인할 수 있었다(Fig. 4B). 기기분석을 통해 실제로 엽록소 함량을 측정했을 때 광조건에서는 무처리 대비 82% 감소되었으나 암조건에서는 거의 영향이 없는 것으로 나타났다(Fig. 5). 따라서 G-0299 배양 여액 농축 시료의 살초효과는 반드시 광조건 하에서만 발현된다는 사실을 다시 한번 확인할 수 있었으며, 엽색 백화 또는 갈변 현상으로부터 세포막 파괴를 유도할 가능성이 있을 것으로 판단되었다.
Fig. 4.
Effect of the isolate G-0299 on chlorophyll content of D. ciliaris leaf tissues under light and dark condition by leaf disc assay. Chlorophyll loss in treatment of culture filtrate by leaf disc assay in the light condition (B) was much higher than in the dark condition (A). The representative pictures were taken 48 hours after treatment.
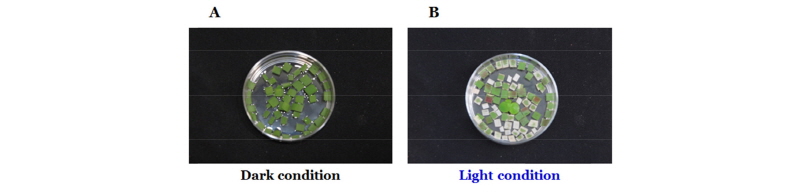
Fig. 5.
Effect of the isolate G-0299 on chlorophyll loss from D. ciliaris leaf tissues under light and dark condition. Chlorophyll content was determined after 48 hours of exposure to 120 μmol m-2 sec-1 PAR at 25°C. Chlorophyll was extracted and assayed according to the procedure of Hiscox and Israelstam. The tissues from the dishes were soaked for 24 h in darkness in 10 ml of dimethyl sulfoxide at room temperature. Total chlorophyll in extracts was determined spectrophotometrically.
이상의 실험 결과 방선균 G-0299는 바랭이에 대해서만 강력한 살초력을 갖고 있으며(Table 1, 2 and Fig. 1, 2), 이와 같은 바랭이에서의 살초력은 광조건하에서만 발현되는 독특한 살초특성을 확인할 수 있었다(Fig. 3). 또한, 광조건에서 경엽처리 시 24시간 이내의 외형적인 살초증상을 볼 때 약효발현 속도가 매우 빠르다는 것을 알 수 있었으며, 주요 살초증상은 처리된 잎에서 고사가 진행되었고, 이후 완전고사 되지 않고 남아 있는 개체에서는 백화현상이 발현되었다(Fig. 1).
이러한 특성을 보이고 있는 방선균 G-0299의 작용기전에 관해 화본과 잡초에 대한 살초효과로부터 화본과 선택 제초제인 지방산 생합성을 저해하는 ACCase 저해제(Lichtenthaler et al., 1989; Secor et al., 1989)와의 유사성을 고려해 볼 수 있을 것이다. 그러나 본 실험에서 발굴한 방선균 G-0299의 경우 화본과 잡초 중에서도 바랭이에 대해서만 살초력을 발휘하고 있기 때문에(Table 3) ACCase 저해제의 작용기전과는 다를 것으로 판단되었다. 또한, 약효발현 속도가 매우 빠를 뿐만 아니라 주요 살초증상이 고사나 백화증상이며, 광조건에서만 제초활성이 나타나고 엽록소 생합성이 저해된다고 하는 결과로부터 광합성 저해제(Wessels and van der Veen, 1956; Itoh and Iwaki, 1989) 또는 protox 저해제(Derrick et al., 1988)와 동일한 작용기전을 유추해 볼 수 있을 것이다. 그런데 상기 두 유형의 제초제 살초특성은 화본과잡초에 비해 상대적으로 광엽잡초에 대한 효과가 우수하며, 처리된 부위에서만 증상이 나타나는 접촉형으로 식물체 내에서의 이행이 상당히 제한적이라서 약제처리 후 일정기간이 경과하면 재생(recovery)된다(Herbicide handbook, 1994). 이에 반해 방선균 G-0299의 경우 화본과잡초 중에서 바랭이에서만 살초력이 발현되고 있으며, 약제처리 후 완전 방제되는 처리농도에서는 일정기간 후에도 재생되지 않는 등의 살초특성을 고려하면 상기 두 유형의 제초제와도 다른 작용기전을 발휘할 가능성이 높을 것으로 사료된다. 또한, Choi et al. (1999)에 의하면 화본과 작물인 보리와 밀 간에도 diphenyl ether계 제초제 oxyfluorfen에 대한 감수성 정도의 차이가 있다고 보고하고 있어 화본과잡초 중에서 바랭이에 대해서만 제초활성을 보이고 있는 본 후보소재는 protox 저해제와의 작용기전 상관성을 설명하기는 곤란한 것으로 판단되었다. 따라서 본 연구에서 발굴한 제초활성 후보소재 G-0299균의 보다 상세한 살초기전에 관해서는 추가 연구를 통해 구명되어야 할 것이다.