Abstract
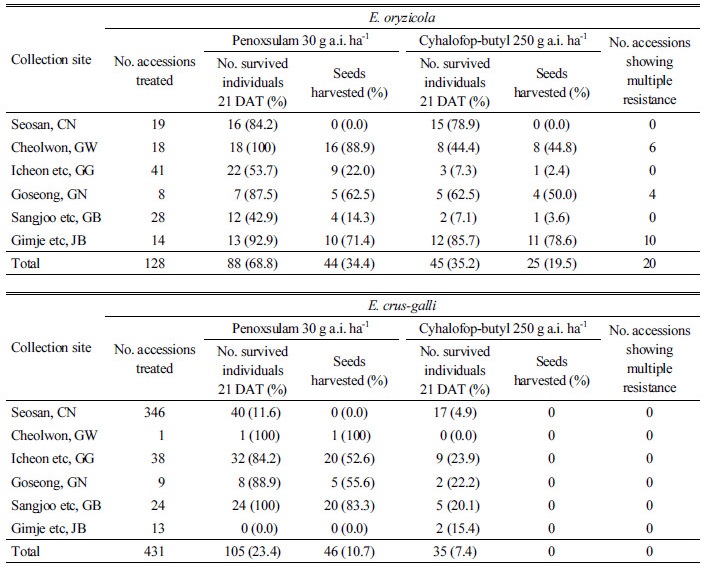
Herbicides are important weed control tools for increasing crop yields and the efficiency of crop production. As the use of herbicides increases, the occurrrence of herbicide-resistant weeds has been an increaing problem. In Korea, since the first occurrence of acetolactate synthase (ALS) inhibitor resistant Monochoria korsakowii was reported in the Seosan reclaimed paddy field in 1998, resistance has been reported in 14 weed species, including Echinochola spp. and their populations are gradually increasing. The objective of this study is to investigate the nationwide occurrence of ALS and Acetyl-CoA Carboylase inhibitor resistant Echinochloa spp. in Korea. In 2013, 2014, and 2015, we collected 594 accessions of Echinochloa spp. in Korean rice fields except for Jeonnam and Chungbuk provinces. They were then treated with the recommended rates of penoxsulam and cyhalofop-butyl. We harvested seeds from 45 accessions of E. oryzicola in the case of cyhalofop-butyl treatment. Also, 44 and 46 accessions of E. oryzicola and E. crus-galli survived and their seeds were harvested after penoxsulam treatment. Twenty accessions of E. oryzicola survived from both herbicides inferring possible multiple resistance. Two accessions out of 20 inferred from possible multiple resistance survived after cyhalofop-butyl treatment at a dose of 500 g a.i. ha-1. Seeds of herbicide resistant populations will be provided and utilized for further research.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the project from the Cooperative Research Program for Agricultural Science & Technology Development of the Rural Development Administration, Korea under Grant number PJ012457.
Figures & Tables