Abstract
Trinexapac-ethyl (TE) is a plant growth retardant using to regulate turfgrass growth in golf course during summer season. This study was conducted to investigate effects of various TE application on growth inhibition and visual quality in creeping bentgrass (
Figures & Tables
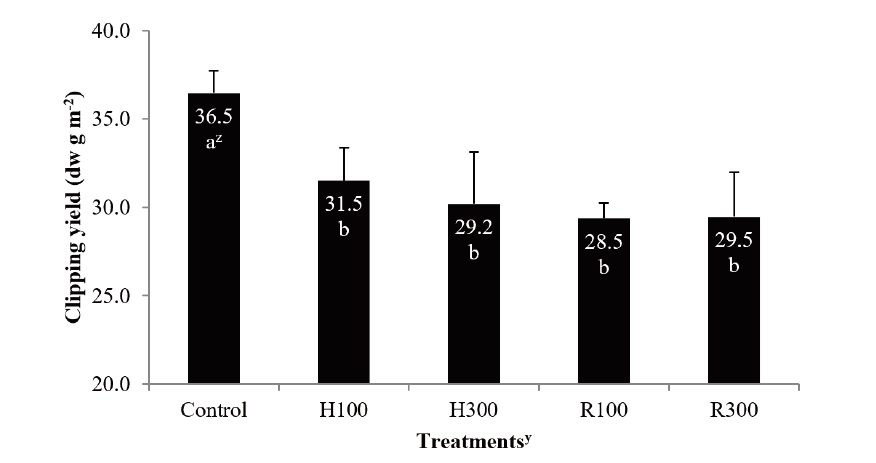
Fig. 1. Clipping yield of creeping bentgrass in pot after application trinexapac-ethyl (TE).


