Abstract
In October 2018, symptoms of the spring dead spot (
Figures & Tables
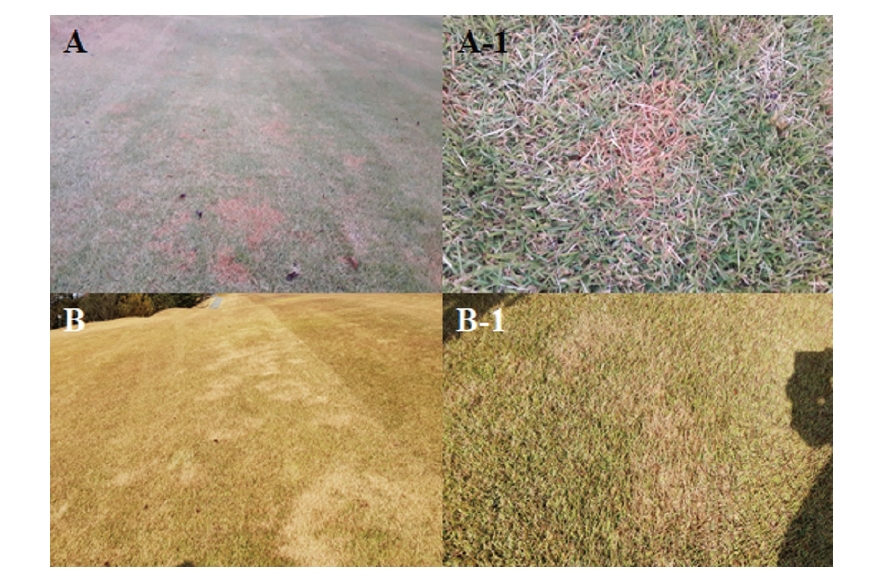
Fig. 1. Disease symptoms on zoysiagrass infected by spring dead spot appeared in the fall season in Korea. A: Observed on Oct. 30; A-1: Close-up view of lesion; B: Observed on Nov. 12; B-1: Close-up view of lesion.


