Abstract
This study was conducted to evaluate effects of bio-sulfur on control of large patch disease caused by
Figures & Tables
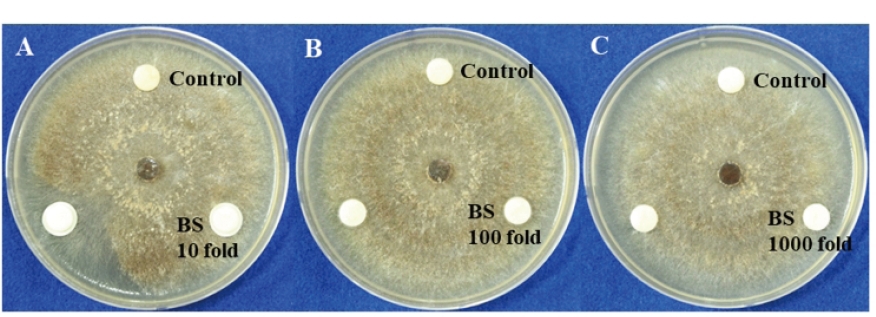
Fig. 1. In vitro test of antifungal activity of bio-sulfur (BS) against R. solani AG2-2 (IV). A: BS 10 fold; B: BS 100 fold; C: BS 1,000 fold.


