서 언
한지형 잔디의 생육적온은 약 15.5-24℃로 여름철 고온기에는 생육이 불량하고 하고현상이 발생한다(Ahn et al., 1992). 골프장의 그린그라운드에 식재된 크리핑 벤트그래스(Agrostis palustris H.)는 여름철에 잦은 강우로 토양에 수분이 많아 웃자라게 되고, 적절한 시기에 깎기작업을 수행하지 못하므로 적절한 예고관리가 어려우며(Lee et al., 2010), 답압에 대한 저항성이 약해지므로 생장조정제를 통한 잔디 예고관리에 관한 연구가 진행되어 왔다(Lee et al., 2008; Tae et al., 2010).
현재 골프장에서 사용할 수 있는 생장조정제는 trinexapac-ethyl과 prohexadione-calcium이다. Trinexapac-ethyl과 prohexadione-calcium은 cyclohexadione계 생장조정제로서 지베렐린 생합성을 억제하여 잔디의 절간생육을 억제함으로써 잔디지상부의 생장을 억제한다(March et al., 2013; Tae et al., 2010). 잔디의 생장조정제에 대한 연구는 주로 trinexapac-ethyl를 중심으로 잔디에 대한 생장 억제 효과(Tae et al., 2010) 및 살포효과(Cho et al., 2019)에 대한 연구가 이뤄졌다. Prohexadione-calcium는 한국잔디(Zoysia japonica)에서 처리하였을 때 절간 생장을 억제하여 지상부의 생육 억제 효과를 나타낸다고 보고하였다(Lim et al., 2011).
Cyclohexadione계 생장조정제인 trinexapac-ethyl와 prohexadione-calcium는 골프장 잔디의 예고관리를 위해 사용되는 생장조정제이며(March et al., 2013; Tae et al., 2010), 크리핑 벤트그래스에 처리 후 일시적으로 잔디 품질이 감소할 수 있으므로 잔디 생육을 고려한 적절한 처리방법이 필요하다(Kim et al., 2019; Wherley and Sinclair, 2009). 특히 한지형 잔디가 식재된 국내 골프장에서 생장조정제를 사용하는 시기가 고온다습한 여름철이므로 생장조정제의 처리에 의한 약해가 발생할 수 있다(Ahn et al., 1992). 그러므로 현재 등록된 계열의 생장조정제가 아닌 다른 작용기작을 갖는 생장조정제의 선발이 필요하다.
생장조정제 중에서 mepiquat chloride는 목화(Gossypium hirsutum)에서 생장을 억제시키고, 목화의 생산과 품질을 향상시킨다(Zhao and Oosterhuis, 2000). 작물보호제 지침서에 따르면 mepiquat chloride는 국내 포도(Vitis vinifera) 작물에서 착립 증진이나 적심 노력 절감을 목적으로 등록된 약제이나, 잔디에서의 생장 억제 효과에 대한 연구는 진행된 바 없다. 따라서 본 연구는 크리핑 벤트그래스에서 생장조정제 mepiquat chloride의 처리에 따른 생육 억제 및 잔디 품질의 변화를 조사하여 mepiquat chloride의 활용가능성을 평가하고자 실험이 수행되었다.
재료 및 방법
시험기간 및 공시재료
포트시험은 경상남도 합천읍 소재의 H사의 시험포장에서 2019년 5월부터 3개월 동안 수행되었고, 공시잔디는 2018년 파종하여 약 1년간 관리한 크리핑 벤트그래스(A. palustris Huds) ‘Penn A-1’ 품종을 이용하였다. 시험에 사용한 토양은 USGA 규격에 적합한 입경분포를 갖는 모래를 상토로 이용하였고, 잔디 생육을 위해 요소(N 46%, Namhae Chemical Co., Ltd., Yeosu, Korea)를 이용해 전층 시비하였다. 공시약제는 메피쾃클로라이드 액제(mepiquat chloride 44%, Taejun Agrotech Co., Ltd., Seongnam, Korea)와 트리넥사팍에틸 미탁제(trinexapac-ethyl 26.6%, Sygenta Koera Co., Ltd., Seoul, Korea)를 이용하였다.
처리구 설정 및 잔디관리
상토의 조성은 토양 개량제를 혼합하지 않은 공시 모래를 시험용 포트(diameter 25 cm, depth 15 cm)에 충진한 후 수돗물을 이용하여 5시간동안 물다짐 후 사용하였다. H사의 증식 포장에서 홀커터(diameter 10.8 cm)를 이용하여 채취된 크리핑 벤트그래스를 5 cm 깊이로 절단한 후 시험용 포트에 5월 31일에 이식하였다. 시비는 포트 조성 시 요소 8.7 g·m-2 (4 N·a.i.·g·m-2)를 1회 전층 시비하였다.
처리구는 mepiquat chloride와 trinexapac ethyl를 처리하지 않은 무처리구(control, non-treatment of growth retardant), 대조약제로서 trinexapac-ethyl를 처리한 관행 대조구(RT, reference treatment; 0.01 a.i.·mL·m-2), mepiquat chloride의 처리량에 준하여 추천량의 반량을 처리한 반량 처리구 (HM, half dose of Mepiquat chloride [MC]; 0.033 a.i.·mL·m-2), 추천량을 처리한 정량 처리구(RM, recommendation dose of MC; 0.066 a.i.·mL·m-2) 및 추천량의 2배를 처리한 배량 처리구(DM, double dose of MC; 0.132 a.i.·mL·m-2)를 설정하였고, 수돗물에 150 mL에 희석하여 희석액 150 mL·m-2을 휴대용 압축 분무기(Trigger sprayer 700, Apollo Industrial Co., Ltd., Siheung, Korea)로 6월 11일에 엽면처리하였다. 실험구 배치는 완전임의배치법으로 하였고, 처리당 4반복으로 하였다. 시험기간 동안 병해충은 발생하지 않아 작물보호제는 처리하지 않았으며, 관수는 스프링클러를 이용하여 1일 2회 총 30분간 실시하였다.
잔디 생육조사
잔디 생육조사는 처리구별 엽색 지수, 엽록소 지수, 가시적 잔디 품질, 잔디 초장 및 잔디 예지물을 조사하였다. 엽색 지수와 엽록소 지수는 각각 turf color meter (TCM 500, Spectrum Technologies, Inc., Plainfield, IL, USA)와 chlorophyll meter (CM 1000, Spectrum Technologies, Inc., Plainfield, IL, USA)를 이용하여 측정하였고, 가시적 잔디 품질은 National Turfgrass Evaluation Program (NTEP)에서 제시한 방법에 준하여 조사하였다(1=worst, 9=best and 6=acceptable). 잔디 초장은 측정용 자를 이용하여 토양표면으로부터 경엽의 길이를 측정하였다. 엽색 지수, 엽록소 지수, 가시적 잔디 품질 및 잔디 초장은 6월 11일부터 7일간격으로 5회 조사하였다. 잔디 예지물 채취는 시험이 종료된 7월 10일에 수행하였고, 70% 에탄올로 잘 소독된 가위를 이용하여 채취한 후 70℃ 건조기(VS-1203PJ-300, Vision Scientific Co., Ltd., Daejeon, Korea)에서 24시간 건조하여 건물중을 측정하였다.
통계분석
통계처리는 SPSS (ver. 12.1, IBM, New York, USA)를 이용하여 Duncan 다중검정과 T 검정을 통해 처리구간 평균값의 유의차를 검정하였고, 단순상관을 통해 요인별 상관성을 분석하였다.
결과 및 고찰
Mepiquat chloride 처리 후 잔디 품질 변화
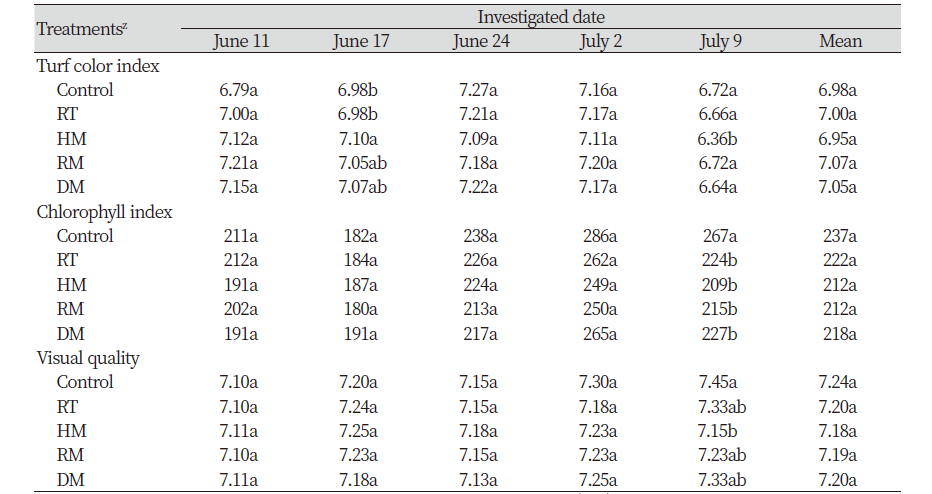
생장조정제 처리 전인 6월 11일 조사에서 무처리구(control), 대조구(RT) 및 mepiquat chloride 처리구들(HM, RM, DM)의 엽색 지수, 엽록소 지수 및 가시적 잔디 품질은 통계적으로 유의적인 차이를 나타내지 않아 시험을 수행하기에 적합하였다(Table 1).
엽색 지수 조사결과, mepiquat chloride 처리 후 7일이 경과한 후 무처리구나 대조구(RT)와 비교할 때, HM 처리구는 엽색 지수가 높았고, RM과 DM 처리구는 통계적으로 유의적인 차이를 나타내지 않았다. 이후 6월 24일, 7월 2일 및 7월 9일 조사에서는 무처리구나 대조구(RT)와 통계적으로 유의적인 차이를 나타내지 않았다. 또한, 시험기간 동안 측정된 엽록소 지수는 무처리구나 대조구(RT)를 비교할 경우 통계적으로 유의적인 차이를 나타내지 않았다. 하지만 온도가 높은 7월 9일 조사에서는 무처리구와 비교하여 trinexapac-ethyl 및 mepiquat chloride 생장조정제 처리구에서 엽록소의 상대적 감소가 보였으나 실험기간 전체적으로 엽록소 함량의 심각한 감소 수준은 아닌 것으로 판단되었다. 가시적 잔디 품질은 6월 17일, 6월 24일 및 7월 2일조사에서는 무처리구와 비교할 때, 대조구(RT) 또는 mepiquat chloride 처리구 사이에 통계적으로 유의적인 차이를 나타내지 않았으나, 7월 9일 조사에서는 HM 처리구에서 잔디 품질이 낮았고, 대조구(RT), RM 및 DM 처리구와는 통계적으로 유의적인 차이를 나타내지 않았다. 이는 가시적 잔디 품질 조사 시 기온이나 토양수분환경과 같은 잔디의 생육의 조건의 변화에 의한 것으로 판단된다(Lee et al., 2006). 그러나 실험 기간 전체 동안 무처리구, 대조구(RT), RM 및 DM 처리구의 가시적 잔디 품질은 HM 처리구와 통계적으로 유의적인 차이를 나타내지 않았다. 따라서 시험기간동안 측정된 엽색 지수와 엽록소 지수 및 가시적 잔디 품질의 평균값으로 비교하였을 때 mepiquat chloride 처리구들은 기존의 생장조정제로 이용되는 trinexapac-ethyl 처리구(RT; 대조구)나 무처리구와 통계적으로 유의적인 차이를 나타내지 않아 잔디의 가시적 품질에 영향을 미치지 않았고, mepiquat chloride의 처리에 의해 크리핑 벤트그래스에서 약해가 발생하지 않는다는 것을 확인할 수 있었다.
Mepiquat chloride 처리 후 생장 억제 효과
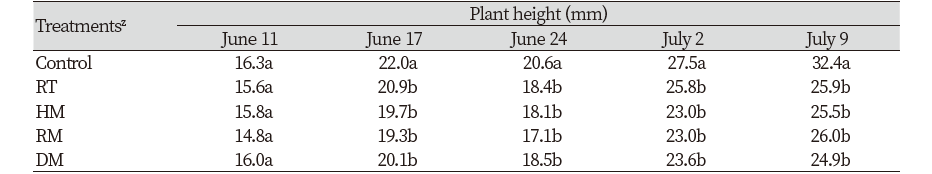
생장조정제 처리 전인 6월 11일 처리구의 초장은 14.8-16.3 mm로 통계적으로 유의적인 차이를 나타내지 않아 생장조정제의 처리 효과를 평가하기에 적합하였다(Table 2). 시험 전 잔디의 초장은 약 15.6±1.2 mm이었고, 약제처리 4주 경과 후에는 무처리구, 대조구(RT), HM, RM 및 DM 처리구에서 각각 32.4, 25.9, 25.5, 26.0, 24.9 mm을 나타내어 생장조정제 trinexapac-ethyl와 mepiquat chloride의 처리구에서 잔디 초장은 유의적으로 감소함을 알 수 있었다. 생장조정제를 처리한 대조구(RT), HM, RM 및 DM 처리구의 잔디 초장은 무처리구보다 각각 20, 21, 20, 23%씩 감소하였고, 생장조정제의 비교 처리를 위해 이용된 대조구(RT)와 HM, RM 및 DM 처리구 간의 잔디 초장 비교에서는 통계적으로 유의적인 차이를 나타내지 않았다.
Mepiquat chloride 처리 후 크리핑 벤트그래스의 생장 억제 효과를 평가하기 위해 시험 종료 후 수거된 잔디 예지물의 건물중을 조사하였다(Fig. 1). 생장조정제 처리 후 4주 경과하였을 때, 무처리구, 대조구(RT), HM, RM 및 DM 처리구의 잔디 예지물은 각각 31.6, 18.0, 14.0, 14.5, 19.4 g·m-2인 것으로 조사되어 처리구간 통계적으로 유의적인 차이를 나타내었다. 무처리구와 비교할 때 대조구(RT), HM, RM 및 DM 처리구의 건물중은 각각 43, 56, 54, 39%씩 감소하여 mepiquat chloride 처리에 따라 잔디 생육량이 감소가 된 것을 확인하였다. Mepiquat chloride 처리구들의 잔디 예지물량은 대조구(RT)와 비교해 볼 때 통계적으로 유의적인 차이를 나타내지 않아 mepiquat chloride의 처리와 trienxapac-ethyl의 처리에 의한 차이는 확인할 수 없었다.
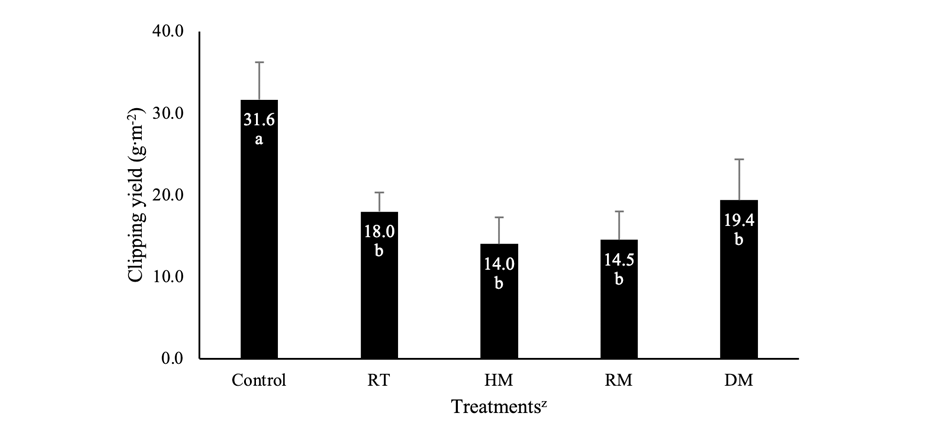
Fig. 1. Clipping yield of creeping bentgrass after application of mepiquat chloride in pot experiment. RT: Reference trinexapac-ethyl; HM: Half dose of Mepiquat chloride (MC); RM: Recommendation dose of MC; DM: Double dose of MC. z Treatments were as follows; Control (non-treatment of plant growth regulator), RT (trinexapac ethyl [TE] 0.01 a.i.·g·m-2; 2,500 fold dilution), HM (MC 0.033 a.i.·g·m-2; 2,000 fold dilution), RM (MC 0.066 a.i.·g·m-2; 1,000 fold dilution), DM (MC 0.132 a.i.·g·m-2; 500 fold dilution). TE and MCs were applied on creeping bentgrass on June 11 in 2019. Error bars indicates standard deviation and different letters indicates significant different at P≤0.05 level according to Duncan’s multiple range test.
고찰
지베렐린 생성을 억제함으로써 식물의 생장을 억제하는 cyclohexadione계 식물생장조정제인 trinexapac-ethyl은 잎으로 흡수되어 생장점에서 작용하여 절간생장에 영향을 주는 생장억제물질이다(Tae et al., 2010; Tomlin, 1995). trinexapac-ethyl의 처리는 크리핑 벤트그래스의 초장 및 지상부 생장을 저해하여 잔디 예지물을 감소시키고(Wherley and Sinclair, 2009), 엽면적과 잔디의 증산량이 감소하여 수분손실이 감소되며, 내건성이 증진되는 것으로 보고되고 있다(McCann and Huang, 2007). 따라서 여름철 고온 기에 크리핑 벤트그래스의 건조 피해를 줄이고, 예초 회수를 줄이기 위한 관리 방법으로 생장조정제의 이용은 골프장 그린 관리에서 효과적인 관리 선택이 될 수 있다(Tae et al., 2010)
Kim et al. (2019)은 trinexapac-ethyl 처리 시 약 20% 정도 잔디 예지물이 감소하여 생장 억제 효과가 인정된다고 보고하였고, 본 연구에서도 잔디 예지물이 약 43% 정도 감소하여 생장 억제 효과가 확인되었다(Fig. 1). Kim et al. (2019)의 연구와 본 연구에서 잔디 예지물량의 차이를 나타낸 것은 크리핑 벤트그래스는 생육 시기에 따라 지상부의 생육이 차이를 나타내고(Ham et al., 2010), 시기별 환경조건에 따라 생장조정제의 처리 효과가 다르기 때문으로 판단된다(Cho et al., 2019; Kim et al., 2019). 본 연구에서 이용된 mepiquat chloride 처리구들의 예지물 감소율은 약 39-56% 정도로 trinexapac-ethyl과 유사한 생장 억제 효과를 보여 mepiquat chloride는 잔디에서 trinexapac-ethyl를 대체할 가능성이 있는 안전한 생장조정제 중 하나로 판단된다(Fig. 1). 그러나 현재 국내에서는 잔디용으로 고시가 되지 않아 mepiquat chloride가 잔디에 사용이 고시되도록 선행 과제가 필요하다고 판단된다.
Mepiquat chloride는 지베렐린 생성을 억제하는 quarternary ammonium계열의 생장조정제이다(Wang et al., 1995). Mepiquat chloride의 작용 기작은 지베렐린 생성량을 억제하여 세포의 신장과 절간의 생장을 저해한다(Gu et al., 2014). 본 연구에서 mepiquat chloride를 처리한 경우 크리핑 벤트그래스의 초장은 약 20-23%정도 감소하여 mepiquat chloride처리가 지상부의 생장을 억제하는데 효과가 있음을 보여주었다(Table 2). 또한 시간의 경과에 따른 초장의 변화를 통해 처리구별 회귀식을 조사한 결과는 Table 3에 제시하였고, R2값이 0.96이상으로 높은 상관관계를 나타내었다. Table 3에 제시된 식을 이용하여 mepiquat chloride처리 후 무처리구의 28일차 초장까지 HM, RM 및 DM가 자라는데 소요되는 예상기간은 각각 50.2일, 45.2일 및 66.1일 정도로 예측되었다. 그러나 mepiquat chloride의 초장 억제 효과를 정확하게 예측하고 평가하기 위해서는 잔디 생육 시기별 mepiquat chloride의 처리에 의한 잔디의 생육 억제 정도에 대한 보완 연구가 필요한 것으로 생각된다. 선행연구에서 Kim et al. (2019)은 trinexapac-ethyl 처리 시 크리핑 벤트그래스의 초장 억제 효과를 10% 정도로 보고하였으나, 본 연구에서 trinexapac-ethyl 처리시 초장 억제 효과는 약 20% 정도로 나타나 잔디의 생육 시기와 조건에 따라 차이를 나타내었기 때문이다(Table 2).
Kim et al. (2019)은 trinexapac-ethyl의 처리량에 따라 잔디의 초장과 잔디 예지물은 부의 상관성을 나타낸다고 보고하였다. 본 연구에서도 mepiquat chloride의 처리량과 잔디의 생장요인들 간의 상관관계조사에서 잔디 예지물에서는 부의 상관관계를 나타내어 Kim et al. (2019)의 결과와 유사한 경향을 나타내었으나, 초장에서는 통계적으로 유의적인 차이를 나타내지 않아 Kim et al. (2019)의 결과와 차이가 있었다(Table 4). 이는 본 연구에서의 mepiquat chloride 처리량이 잔디가 아닌 포도에 적용하는 추천량을 처리하였기 때문으로 판단된다. 본 연구에서 처리된 mepiquat chloride의 농도별 잔디의 초장의 변화가 나타나지 않았던 Table 4의 결과를 고려할 때, 현재 사용한 mepiquat chloride의 처리농도는 잔디 생육 억제 효과는 있으나 농도별 차이를 나타내지 않았다. 따라서 포도에 적용된 농도보다 낮은 농도를 잔디에 처리하여 처리 농도별 잔디의 초장과 예지물의 변화에 대한 조사를 통해 최적 처리량을 결정하는 연구가 추가로 진행되어야 할 것으로 판단된다. 또한 잔디의 초종에 따라 그 반응 정도는 다르게 나타날 수 있으므로 향후 켄터키 블루그래스에 mepiquat chloride 처리 후 생장 억제 효과 등 다른 한지형 잔디에서의 효과 여부도 조사할 필요가 있을 것으로 보인다(Hong et al., 2009; Tae et al., 2010). 그 이외에도 mepiquat chloride를 아마(Linum ustitatissimum)에 처리한 경우 가지의 발생이 증대되고, trinexapac-ethyl처리 시 잔디 밀도가 증가되어 생장조정제 처리 후 식물의 가지나 줄기가 증가하는 결과를 나타내었다(Kim et al., 2013; Tae et al., 2010). 본 연구 결과에서는 잔디 밀도 조사는 수행되지 않아 확인할 수 없었으므로 mepiquat chloride를 추가 실험을 통해 잔디의 지상부와 지하부의 생육 및 밀도 조사 등 보완이 필요할 것으로 보인다.
Authors Information
Hyeok-Jae Heo, School of Ecology & Environmental System (Major in Plant Resource Environment), Kyungpook National University, Daegu 41566, Korea, Master
Eun-Hye Park, https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8711-5043
Jin-Ho Kim, School of Ecology & Environmental System (Major in Plant Resource Environment), Kyungpook National University, Daegu 41566, Korea, Professor
Jeong-Ho Youn, Hanul Co. Ltd. Hapcheoun 38453, Korea, CEO
Young-Sun Kim, Division of Life & Environmental Science (Horticulture Major), College of Natural and Life Sciences, Daegu University, Professor, Institute of Basic Science, Daegu University, Researcher
Geung-Joo Lee, Department of Horticulture and Department of Smart Agriculture Systems, Chungnam National University, Professor