Abstract
Various species of plant parasitic nematodes are known to damage turfgrass. However, there are no nematicides registered for the control of turfgrass nematodes in Korea. Therefore, the present study was conducted to investigate the efficacy of some nematicidal active ingredients ([nematicides; abamectin, fluazaindolizine, fluopyram, fosthiazate, imicyafos], microbial nematicide [
Figures & Tables
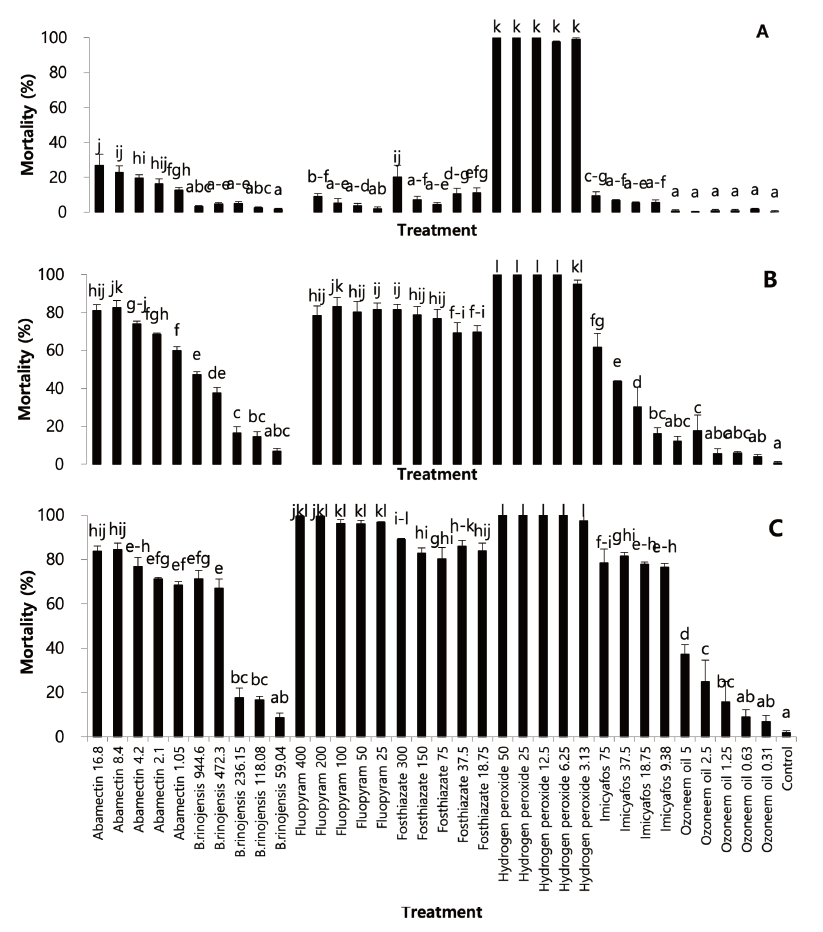
Fig. 1. Control efficacy of some nematicidal agents against turfgrass parasitic nematodes isolated from Kentucky blue grass in tee of Tani country club in multi-well plate (first trial). A: 24 hours after treatment; B: 48 hours after treatment; C: 72 hours after treatment. Nematodes were socked with aquatic suspension of nematicidal materials. Bars on the graph represent means of 4 replicates±SE; bars with the same lowercase letters are not significantly different according to the Tukey’s studentized range (HSD) test (<0.05). Number in treatment is amount of applied nematicides’ active ingredient (ppm).


