서론
식물기생선충은 다양한 경제작물을 비롯하여 수목이나 자연 서식 초본류에도 피해를 주는 중요한 관리 대상 인자의 하나이다. 식물기생선충에 의한 피해는 작물에 따라 차이가 있으나 피해규모는 연간 800억$로 추산되고 있다(Nicol et al., 2011). 식물기생선충은 토양과 식물체에 기생하면서 식물에 직·간접적인 피해를 일으키고 있으나 대부분 크기가 1 mm미만으로 작고, 토양이나 식물체 내에 서식하기 때문에 관찰이 용이하지 않으며 식물체에 외부적 병징 발현이 늦거나 미미하여 피해가 발생하고 있으나 간과되는 경우가 많다.
우리나라에서 식물기생선충에 대한 연구는 1919년 밀(Triticum aestivum)에서 밀알선충(Anguina tritici)에 의한 피해가 보고된 이래 매우 제한적으로 이루어지고 있는데(Choi, 2001) 다양한 식량작물을 비롯하여 약용작물, 수목 등에서 발생과 피해가 보고되고 있다(Choi, 1963; Cho and Han, 1986; Choi et al., 1989; Choi et al., 1992; Park et al., 1992).
잔디에서도 다양한 식물기생선충들이 피해를 주고 있는데 잔디밭에 나타나는 피해는 종자나 잎, 줄기, 뿌리에 기생하여 종자 생산량 감소나 잎의 왜화나 활력 감소, 뿌리 발육 저해 및 괴사, 생장억제, 황화, 위축 등의 다양한 증상으로 나타난다(Couch, 1995).
잔디에 기생하는 선충은 잔디의 초종이나 지역에 따라 다양하게 나타나고 있다. Yokoo (1963)는 일본 Kyushu 골프장 잔디에서 12종류의 식물기생선충을 보고하였고, Fushtey and McElroy (1977)는 캐나다 Southern British Columbia 골프장 잔디에서 10속의 식물기생선충을 보고하였다. Couch (1995)는 잔디 초종별로 구분하여 8과 12속 63종의 잔디기생선충을 발표하였으며 Zeng et al. (2012a)은 North Carolina와 South Carolina의 39개 골프장 잔디에서 15과 22속 29종의 식물기생선충을 보고하였다.
우리나라에서는 잔디를 대상으로 한 식물기생선충에 대한 연구는 매우 제한적으로 이루어졌는데 고구마뿌리혹선충(Meloidogyne incognita)에 의한 잔디 피해가 최초 보고(Choo et al., 1998)된 이후 매우 단편적인 연구만 수행되었다. 잔디 기생선충과 관련된 연구는 다른 작물들에 비해 상대적으로 적고, 우리나라에서 연구 역사도 매우 짧은 편이다. 그러나 한지형 잔디의 이용 증가나 기후변화로 인한 온난화와 같은 요인들은 잔디 기생선충의 피해를 증가시킬 수 있는 위협요인으로 대두되고 있다.
잔디에 피해를 주는 생물적 인자들은 해충과 병, 잡초들이 있는데 우리나라에서 잔디 해충과 관련된 연구현황은 Choo and Lee (2017)에 의해 발표되었는데 13과 33종의 잔디 해충을 보고하였다. 또한 우리나라 잔디에 발생하는 병과 관련된 연구사는 Shim and Lee (2018)에 의해 발표되었는데 병의 종류와 방제용 농약 연구 분야 등을 포함하고 있다. 잔디밭에 발생하는 잡초와 관련 된 연구에서는 문헌조사를 통해 공원 등지의 잔디밭에서 발생하는 잡초 16과 37종과 묘지 잔디밭에 발생하는 잡초 53과 196종이 보고되었다(Lee et al., 2013). 그러나 식물기생선충의 경우 잔디에 피해를 주는 주요한 생물적 인자임에도 불구하고, 해충이나 병리적 측면에서 다루어지지 않아 본 연구에서 우리나라의 잔디 관련 식물기생선충 연구 현황과 향후 연구 방향을 고찰해 보고자 한다.
우리나라 잔디 선충 연구사
우리나라에서 선충 분야 연구 내용을 알아보기 위하여 잔디 선충 관련 논문 검색을 경북대학교도서관 전자자원 통합검색 시스템(https://knu.summon.serialssolutions.com)과 선충학 및 잔디학 관련 분야 학회인 (사)한국응용곤충학회, (사)한국식물병리학회, (사)한국잔디학회, (사)한국원예학회, (사)한국농약과학회의 논문 검색 시스템을 이용하여 조사하였다.
우리나라에서 잔디 선충 관련 연구 자료는 17편에 불가하였는데 이는 2016년까지 우리나라 잔디 해충 관련논문 52편(Choo and Lee, 2017)이나 잔디 병 관련 논문 81편(Shim and Lee, 2018)에 비해 매우 적은 수이다. 17편의 잔디 선충 관련 문헌들 중 16건은 잔디 선충에 대한 직접적인 연구였고, 1편은 식물기생선충 조사에서 기주로 잔디(Zoysia japonica)가 포함된 내용이었다(Choi, 2001).
잔디 선충 연구와 직접적인 관련이 있는 16편 중 골프장 잔디에서 선충에 의한 피해 보고와 관련 된 문헌이 2편(Choo et al., 1998; Kang et al., 2003), 잔디기생선충 방제와 관련 된 문헌이 2편(Na et al., 2021; Kabir et al., 2021) 이었으며 나머지 12편은 선충 분류와 관련된 문헌들이었다.
우리나라에서 잔디에 발생하는 식물기생선충과 관련된 최초 보고는 1998년 한국잔디학회지에 보고된 고구마뿌리혹선충에 의한 잔디(Zoysia japonica)와 금잔디(Z. materella), 버뮤다그래스(Cynodon sp.) 피해에 관한 연구(Choo et al., 1998)였고, 이후 2002년에 골프장 잔디에서 잔디뿌리혹선충(Meloidogyne marylandi)의 발생이 보고되었다(Kang et al., 2002). 2003년에는 골프장에서 6속의 식물기생선충과 목초위축선충(Tylenchorhynochus dubius)에 의한 벤트그라스(Agrotis palustris) 피해가 보고되었는데(Kang et al., 2003) 목초위축선충에 의한 피해는 이후 Khan et al. (2008)에 의해 추가 확인되었다.
2020년에는 골프장 잔디에 발생하는 5종의 우리나라 미기록 선충(Mwamula et al., 2020b, 2020c, 2020d, 2020e, 2020f)과 1종의 신종(Mwamula et al., 2020a)이 발표되어 단일 년도 단위로는 가장 많은 잔디 선충 관련 논문이 출간되었다. 2021년에는 우리나라 미기록 1종의 선충에 대한 보고와 함께(Mwamula et al., 2021b) 우리나라 13개 골프장에서 잔디에 발생하는 12과 28종의 선충이 보고되었는데(Mwamula et al., 2021a) 이는 우리나라의 잔디기생선충의 종류에 대한 최초의 종합적 연구결과였다. 또한 이 시기에 잔디기생선충 방제와 관련된 연구가 수행되었다(Na et al., 2021; Kabir et al., 2021). 2022년에는 2021년에 속(genus) 수준의 분류가 이루어졌던 양잔디짧은침선충(Filenchus cylindricus)에 대한 종 동정 결과가 발표되었고(Mwamula et al., 2022), 2023년에는 소나무나선선충(Rotylenchus pini)이 골프장 잔디에서 분리되어 보고되었다(Mwamula et al., 2023).
잔디 선충 관련 논문들은 식물 병 관련 학술지인 The Plant Pathology Journal과 European Journal of Plant Pathology에 각각 4편씩이 발표되었고, 선충 분야 전문 학술지인 Nematology에 4편이 발표되었으며 (사)한국잡초학회와 (사)잔디학회 공동 학술지인 Weed and Turfgrass Science와 전신인 한국잔디학회지에 3편의 논문이 발표되었다.
우리나라 잔디 선충의 종류
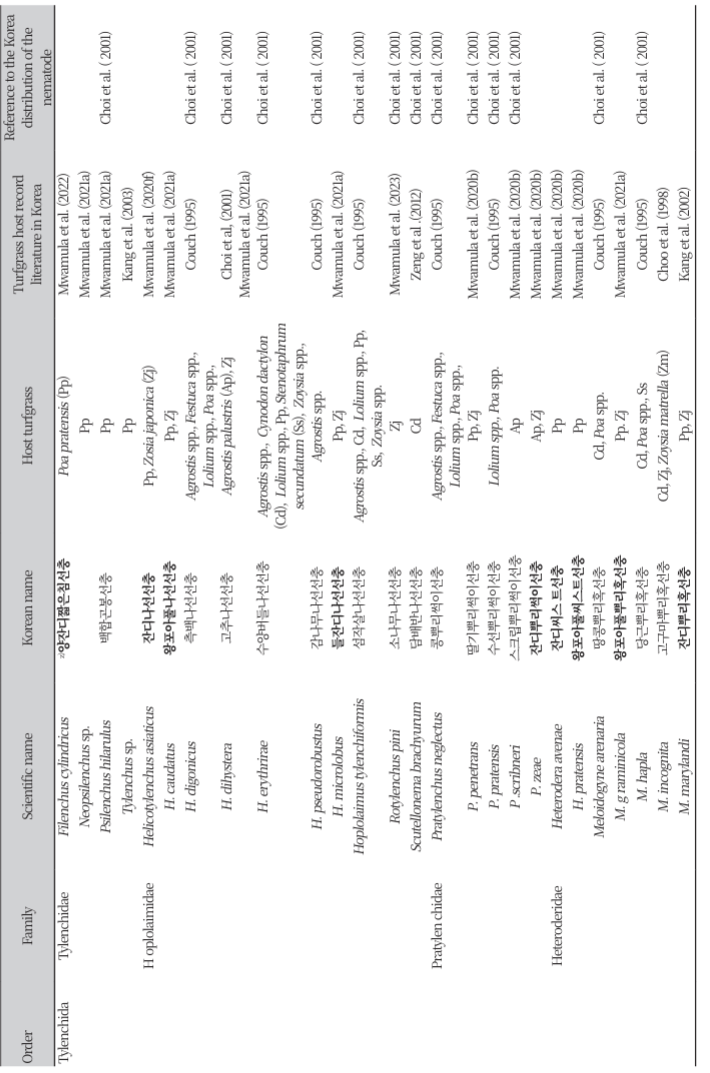
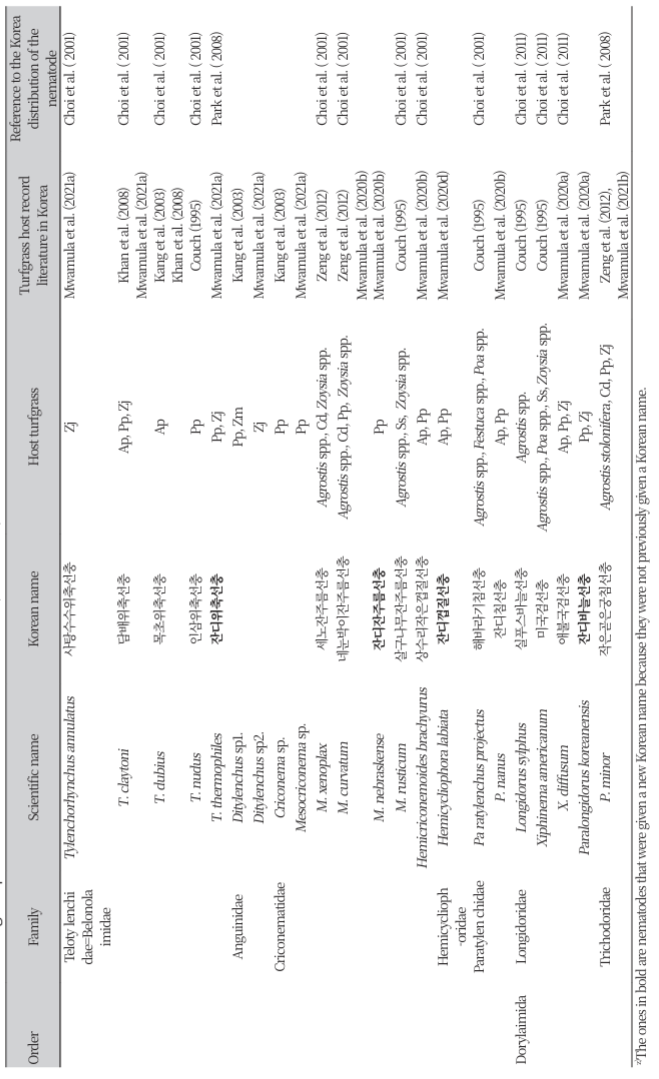
우리나라에 분포하고 있는 식물기생선충에 대한 종합적 보고는 2001년 12과 132종이 보고되었는데(Choi, 2001) 이때 잔디가 채집 식물로 기록되어 있는 선충은 고추나선선충(Helicotylenchus dihystera) 1종에 불과하였으나 이 문헌에는 1998년에 잔디에서 피해가 확인된 고구마뿌리혹선충의 자료(Choo et al., 1998)는 포함되지 않았다. 한편 이 시기에 외국에서는 잔디기생선충으로 기존에 보고 되었지만 우리나라에서는 잔디에서 발견되지 않았고, 다른 식물에서 분리된 기록이 있던 종은 측백나선선충(Helicotylenchus digonicus)을 포함하여 7과 12종이었다(Choi, 2001)(Table 1). 이후 2008년 Park et al.에 의해 작은곧은궁침선충(Paratrichodorus minor)이 제주지역의 감귤밭에서 검출되었는데 이 선충은 후에 미국 골프장 잔디[버뮤다그래스(Cynodon dactylon), 크리핑 벤트그래스(Agrostis stolonifera), 들잔디(Zoysia japonica)]에서 검출되었으며(Zeng et al., 2012b) 우리나라 골프장의 벤트그래스와 들잔디에서 검출이 확인 되었다(Mwamula et al., 2021b) (Table 1).
우리나라 골프장 잔디에서 검출된 12과 29종의 식물기생선충이 Mwamula et al. (2021a, 2022, 2023)의 연구에 의해 추가되어 우리나라의 잔디 기생선충은 2목 11과 47종류(Table 1)로 확인되었다. 이들 중 양잔디짧은침선충과 잔디나선선충(Helicotylenchus asiaticus), 왕포아풀나선선충(Helicotylenchus caudatus), 들잔디나선선충(Helicotylenchus microlobus), 잔디뿌리썩이선충(Pratylenchus zeae), 잔디씨스트선충(Heterodera avenae), 왕포아풀씨스트선충(Heterodera pratensis), 왕포아풀뿌리혹선충(Meloidogyne graminicola), 잔디위축선충(Tylenchorhynchus thermophiles), 잔디잔주름선충(Mesocriconema nebraskense), 잔디껍질선충(Hemicycliophora labiata), 잔디침선충(Paratylenchus nanus), 잔디바늘선충(Paralongidorus koreanensis)은 2001년 Choi의 우리나라 선충 목록에 없던 미기록 선충들로 미기록 종에 대한 분류학적 영어 논문은 출간이 되었으나 국명이 부여되지 못하여 본 연구에서 학명에 대한 국명을 새로이 부여한다. 국명의 부여는 선충이 발견된 기주명과 선충의 형태적 특성에 기반한 과명을 기준으로 하였으며 선충의 분류학적 특성은 선행 논문들에 자세히 기술되었다.
우리나라 잔디에서 선충에 의한 피해와 방제 관련 연구
식물기생선충에 의한 잔디 피해 양상은 잔디의 초종과 선충의 종류에 따라 다양하게 나타난다(Couch, 1995). 우리나라에서 식물기생선충에 의한 잔디 피해양상과 관련된 연구는 특정 선충에 의한 잔디 피해 증상을 보고한 논문과 전체적으로 생육저하 현상을 보이는 잔디에서 식물기생선충을 분리하여 보고한 연구로 구분할 수 있다. 특정 선충 피해와 관련된 연구로는 고구마뿌리혹선충의 경우 잔디와 금잔디, 버뮤다그래스에서 황화, 시들음, 생육저하가 일어난다고 하였으며(Choo et al., 1998), 잔디뿌리혹선충은 선충에 기생 된 잔디는 뿌리 끝이 잘린 것 같이 뭉뚝하고, 갈변되며 지상부 황변 피해가 유발된다고 하였다(Kang et al., 2002). 목초위축선충의 밀도가 높은 벤트그래스에서는 황화현상과 함께 시들음 증상이 나타났고(Kang et al., 2003), 양잔디짧은침선충이 발생한 벤트그라스에서는 옅은 엽색 잔디들이 불규칙적인 패취를 형성하였다(Mwamula et al., 2022). 골프장에서 잔디의 생육이 부진한 곳에서는 핀선충속(Paratylenchus sp.)이나 뽀족꼬리주름선충속(Criconema sp.), 줄기구근선충속(Ditylenchus sp.), 나선선충속(Helicotylenchus sp.), 참선충속(Tylenchus sp.), 궁침선충속(Tylenchorhynchus sp.)의 선충들이 검출되었으며(Kang et al., 2003) 벤트그라스에서 백화와 잔디 잎의 고사, 활력 감소, 잔디의 위축 등의 피해 증상을 보인 곳에서 담배위축선충이 검출되었다(Khan et al., 2008). Mwamula and Lee (2021a)는 골프장에서 잔디의 생장이 부진하거나 잔디 밀도가 상대적으로 낮은 곳이거나 뿌리에 혹이 형성 되었거나 줄기나 잎에 황화 증상 등이 나타나는 곳을 중심으로 채취한 토양 시료에서 12과 28종의 식물기생선충들이 분리되었다.
잔디에 기생하는 식물기생선충에 의한 피해 양상은 개별 종의 피해 특성보다는 과(family) 수준의 피해 양상으로 다음과 같이 대별하고 있다(Couch, 1995). 우리나라에 기록되어 있는 잔디 피해 선충들 중 가장 종수가 많은 잔디나선선충과가 속해있는 나선선충의 경우 선충의 밀도가 높으면 피해 부위가 물러지고, 감염부위가 진갈색으로 된 뒤 외피조직이 와해된다. 뿌리썩이선충과의 선충들은 잔디의 뿌리에 갈변이 나타나다 점차 확대되며 선충 밀도가 높아지면 뿌리가 와해되는 피해가 발생한다. 뿌리혹선충은 뿌리에 혹을 형성하고 씨스트선충은 뿌리의 괴사가 일어난다. 위축선충과의 선충들은 밀도가 높을 경우 잔디의 생장을 억제한다. 환선충과의 선충들은 뿌리 끝뿐만 아니라 측면을 따라서도 괴사가 일어나며 심할 경우 뿌리 전체의 괴사를 유발한다. 침선충과의 선충들은 잔디의 절간이 짧아지고, 위축과 총생을 유발한다. 바늘선충류는 잔디의 세력을 약화시키며 검선충은 지상부 백화현상과 위축이 유발되며 뿌리 발육이 억제되고 심하면 뿌리썩은 증상이 나타난다. 궁침선충류는 성장중인 뿌리에만 감염하여 뿌리 선단부가 없어지거나 신장부위가 소실된다.
식물기생선충의 종류별에 따라 피해양상이 뚜렷이 구별되는 경우도 있지만 선충의 종류나 지역,잔디 초종에 따라 피해 정도나 양상에 차이를 보여 선충에 따라 피해 허용 밀도에 차이를 보이고 있다(Couch, 1995; Jordan and Mitkowski, 2006; Kirkpatrick et al., 2017). Belenolaimus longicaudatus 선충의 경우 토양 500㎤당 9마리 이상이면 잔디에 심각한 피해를 유발시킬 수 있는 밀도이지만 Hoplolaimus galeatus선충의 경우 1000마리 이상이 심각한 피해를 유발시킬 수 있는 밀도로 알려져 있다(Ye et al., 2012). 그러나 개별 선충별로 잔디 초종에 대한 밀도별 피해나 피해 허용 수준에 대한 연구들은 제한적으로 수행되어 왔고(Bekal and Becker, 2000; Plaisance et al., 2015; Settle et al., 2007), 우리나라에서는 이러한 연구가 수행된 바 없다. 따라서 향후 우리나라의 잔디에 우점하는 선충 종의 잔디 초종별 밀도 반응이나 피해양상에 대한 연구가 시급히 필요할 것으로 생각된다.
다양한 식물기생선충들이 잔디에 발생하여 피해를 주고 있음에도 불구하고 잔디기생선충의 방제와 관련된 연구는 2편에 불과하였다(Kabir et al., 2021; Na et al., 2021). Na et al (2021)은 7종의 살선충 제제들을 이용하여 잔디에서 분리한 선충[작은궁침선충과 들잔디나선선충, 잔디바늘선충, 네눈박이잔주름선충(Mesocriconema curvatum), 잔디위축선충]들에 대한 살선충 효과를 실내에서 검증하였고, 켄터키블루그래스로 조성된 골프장 티에서 살선충제의 효과를 검증하여 imicyafos와 fluopyram가 실용적 효과가 있다고 하였다. Faisal et al (2022)는 잔디잔주름선충과 들잔디나선선충이 혼재 된 야외 채집 선충을 이용하여 약제별 반응에 두 선충간 차이가 없음을 규명하였고, 야외 시험에서 살선충별 효과를 검정하여 fosthiazate 처리에서 처리 60일후 86%의 선충 밀도 감소효과를 보고하였다. 식물기생선충에 대한 방제는 다양한 방법들이 적용되고 있으나 골프장 잔디에 발생하여 피해를 주는 식물기생선충을 방제하는 효과적인 현실적 방제방법은 화학적 방제이다(Na et al., 2021). 그러나 현재 우리나라에 잔디에 발생하는 식물기생선충에 등록 된 농약은 뿌리혹선충 방제용으로 등록 된 imicyafos액제와 입제 두 품목에 불과하다(RDA, 2024). 따라서 다양한 선충의 피해를 받고 있는 잔디밭에 적용할 수 있는 방제제 연구와 등록이 필요할 것으로 판단된다.
향후 잔디기생선충 연구 방향
우리나라의 잔디 병 관련 연구논문은 81건에 보고 된 잔디 병은 15종이고, 잔디 병 방제용으로등록 된 살균제는 2018년 461 품목에 달한다(Shim and Lee, 2018). 또한 잔디 해충 관련 연구논문은 2016년까지 52편에 잔디에 해충으로 기록된 종수는 8목 15과 35종이다(Choo and Lee, 2017). 우리나라의 잔디에 피해를 줄 수 있는 선충의 종류는 2목 11과 47종류로 보고된 잔디 병 수의 3배에 달하며 잔디 해충의 종수보다 많은 종이 발생하고 있다. 그러나 잔디 선충의 연구논문은 16건에 불과하여 병이나 해충에 비하여 매우 빈약한 실정이며 잔디밭에서 사용 가능한 농약도 2품목에 불과하여 살균제나 살충제의 품목 수와 현저한 차이를 보이고 있다. 해충이나 각종 식물병(진균, 세균, 바이러스) 연구자들에 비하여 상대적으로 부족한 선충연구자의 부재와 피해의 심각성에 비해 잔디 관리자들의 인식부족, 일반 경제작물에 비하여 상대적으로 연구가 부족한 잔디분야의 연구부족 등으로 인해 잔디 기생선충에 관한 연구가 제한적으로 수행되고 있는 현실이다. 따라서 잔디기생선충에 대한 연구 활성화가 절실히 필요하며 시급한 연구분야는 선충 종별에 따른 잔디 초종별 피해 양상과 피해 허용 밀도 규명, 잔디밭에서 관리 대상 선충에 대한 기초 연구, 실용적 방제 효과가 있는 살선충제의 개발과 적용으로 생각된다. 아울러 선충에 의한 잔디 피해 진단과 예찰 방법에 대한 실제적 교육도 필요한 부분으로 생각된다.
요약
잔디의 생장에 영향을 주는 생물적 인자들은 병과 해충이 있는데 선충도 인자의 하나이다. 식물기생성선충은 다양한 작물에 피해를 주고 있는데 잔디에서도 시들음, 생장억제, 고사 등의 피해를 유발한다. 본 논문은 우리나라에서 잔디 관련 식물기생선충의 연구 현황을 조사하여 향후 잔디선충 관련 연구방향을 제시하고자 수행하였다. 우리나라에서 잔디관련 연구문헌은 2024년 현재까지 17편에 불과하였는데 분류분야가 12건, 방제 분야가 2건 등이었다. 우리나라에 기록되어 있는 잔디기생선충은 2목 11과 47종류였는데 기존에 발표된 논문들이 영문으로 출간되어 잔디에서 발견된 식물기생선충에 대한 한국명이 없어 양잔디짧은침선충을 포함한 13종의 선충에 새로운 한국명을 부여한다. 우리나라에서 잔디밭 선충 방제용으로 등록된 농약은 2품목에 불과하여 뿌리썩이선충이나 씨스트선충 등 피해 우려 선충에 대한 방제제 등록이 필요할 것으로 판단된다. 잔디에 발생하고 있는 선충들의 밀도반응과 피해허용 수준에 대한 연구가 시급히 필요할 것으로 사료된다.
Acknowledgements
본 연구는 한국농림축산식품기술기획평가원(IPET)의 농림축산식품부 지원 농림축산식품융합기술창의형 글로벌 리더 양성과정 연구비(농식품부)(제321001-03호) 지원으로 수행되었다. 본 논문은 제1저자의 석사학위 논문을 기반으로 작성되었다.
Authors Information
Chanki Kwon, Kyungpook National University, Master student
Abraham Okki Mwamula, Kyungpook National University, PhD.
Oh-Gyeong Kwon, Kyungpook National University, Doctor student
Dong Woon Lee, Kyungpook National University, Professor, ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9751-5390