Abstract
This study was conducted to investigate the reduction of rice chlorophyll content and herbicidal effects of clove oil and pine oil, and to identify the components of major organic compounds contained in the plant essential oils. The chlorophyll content of rice after 24, 48, 96, and 168 hours of plant essential oil treatment was 59.9, 54.6, 27.1, and 14.5% in the case of 10 times dilution clove oil, and 47.2, 23.5, 15.7, and 10.9% in pine oil 10 times dilution, respectively. The chlorophyll reduction effect of 10 times dilution of clove oil and pine oil was greater than that of the recommended amount of glufosinate ammonium. As the concentration of the plant essential oil dilution increased, herbicidal effects increased, but the effect was different depending on the weed species. Herbicidal effects was higher in the glass weeds than in the broadleaf weeds, and the control effects on
Figures & Tables
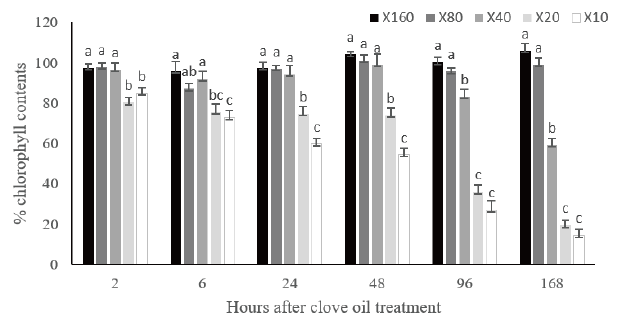
Fig. 1. Effects of essential oil from (clove oil) treatments on contents (%) of chlorophyll in leaves of rice in greenhouse condition. Above, ×160 and so on mean dilution folds. Bars on the graph is standard deviation. a-c: Means within a column followed by the same lowercase letters are not significantly different by Duncan's multiple range test at 5%.


