Abstract
Zoysiagrass is widely used for parks, golf courses, garden and playground in Korea. Development of new varieties of zoysiagrass suitable for field demand is required. This study was conducted to develop new zoysiagrass cultivars ‘Taeji. ‘Taeji’ is a developed new cultivar by polyploidy breeding. To produce ‘Taeji’, after 4 days of germination of the ‘Zenith’ (
Figures & Tables
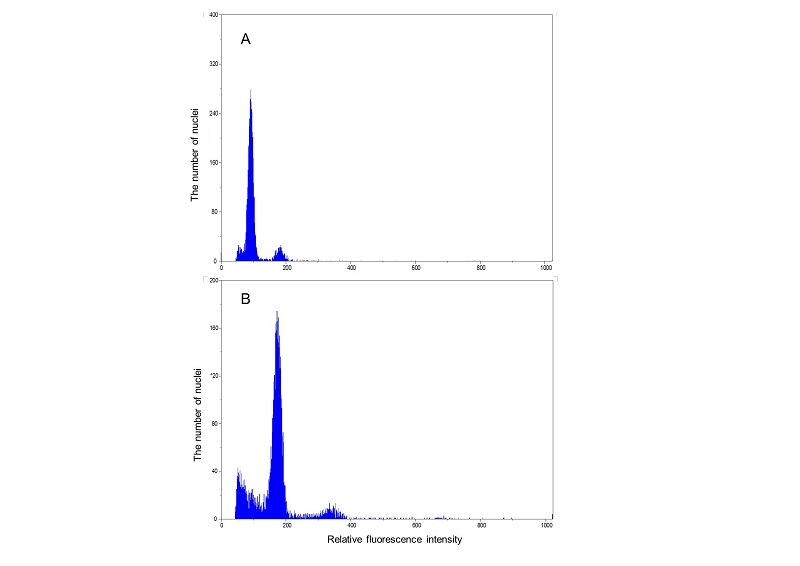
Fig. 1. Flow cytometric histograms of ‘Zenith’ and ‘Taeji’ of Zoysiagrass ( STEUD) of which somatic chromosomes were doubled by colchicine treatment. A: Zenith; B: Taeji.


