Abstract
This study was conducted to evaluate synergy effects of non-ionic surfactant on control of large patch diseases caused by
Figures & Tables
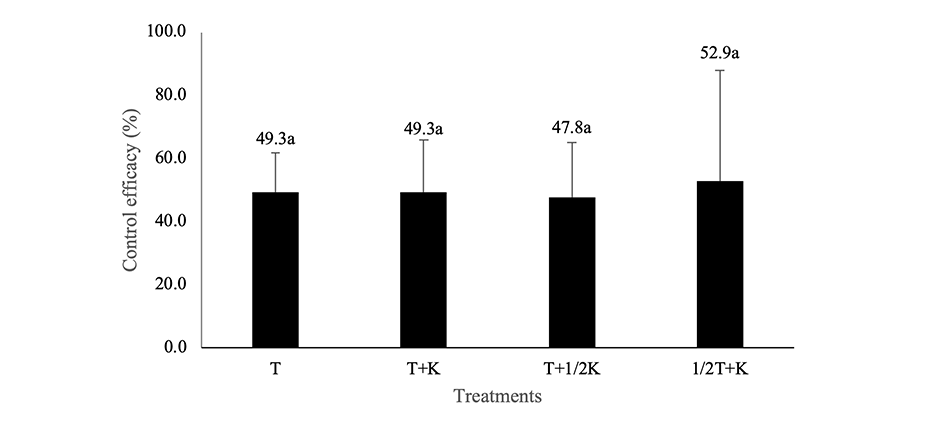
Fig. 1. Control efficacy of large patch in zoysiagrass after applied with non-ionic surfactant or tebuconazole. Error bars indicates standard deviation and different letters indicates significant different at <.05 level according to Duncan’ s multiple range test. Large patch was investigated on July 10. Treatments were as follows. Control: Non-application, tebuconazole (T; 0.125 a.i. T g m), and mixture treatments of non-ionic surfactant (K) and tebuconazole (T+K, 0.125 a.i. T g m+0.25 K g m; T+1/2K, 0.125 a.i. T g m+0.125 K g m; 1/2T+K, 0.063 a.i. T g m+0.25 K g m). Tebuconazole and mixtures of tebuconazole and non-ionic surfactant were applied three times on June 19, June 26, and July 3.


